Performance of black gram varieties to mungbean yellow mosaic disease at different sowing dates under spring and summer condition in western terai of Nepal
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.26832/24566632.2022.0704020Keywords:
Black gram, Growing season, Date of sowing, Yellow mosaic virusAbstract
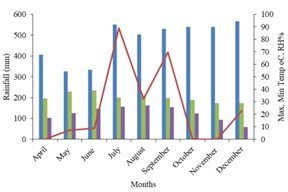
A field experiment was conducted at Grain Legumes Research Program (GLRP), Khajura, Banke, Nepal during spring and summer season 2019 to elucidate the effect of date of sowing and blackgram varieties on mungbean yellow mosaic disease severity and yield. The experiment was conducted in 2 factorial randomized complete block design with 3 replications. Factor A comprised date of sowing (S1= 5th April 2019, S2= 20th April 2019, S3= 5th May 2019, S4= 20th May 2019, S5= 25th July 2019, S6= 10th August 2019, S7= 25th August 2019 and S8= 10th September 2019) and factor B (Variety): V1= Khajura Mas 1 and V2= Rampur Mas. Disease severity was scored in 1-6 scale. Results revealed that mean values for days to disease appearance, disease score and grain yield in spring season sowing was 26 days, 3.72 and 635 kg/ha, whereas for summer season sowing was 14 days, 5.04 and 185 kg/ha. Among the date of sowing, April 5th sown crop recorded minimum mean disease score (3.1) with highest yield (719 kg/ha). Whereas, September 10th sown crop recorded maximum mean disease score (5.1) with lowest yield (174 kg/ha). Black gram varieties showed significant response to mean disease score and yield at early sowing condition but when the sowing date was delayed, there was no significant response of varieties to mean disease score and yield. The contribution of regression (R2 =0.791) and (R2 = 0.655) for spring season and summer season indicate that 79% and 65% of the blackgram yield would be affected by disease for the respective season. Therefore, it is better to sow blackgram in early season to escape mungbean yellow mosaic disease and minimize yield loss.
Downloads
References
Arif, M., Farooq, S., Alasmari, A., Alshehri, M. A., Hashem, M., Alamri, S., & Alabdallah, N. M. (2022). Molecular study of geminiviruses with its complex biology, host-vector interactions, and increasing diversity. Journal of King Saud University-Science, 102051.
Garg, V. K., & Patel, Y. (2018). Influence of weather parameters on population dynamics of whitefly in kharif legumes. Annals of Plant and Soil Research, 20(4): 371-374
Hadiya, H. R., Patel, D. R., Pathak, D. M., & Patel, S. G. (2020). Impact of sowing periods on incidence of sucking pest on summer mungbean. Journal of Entomology and Zoology studies, 8(1), 815-818
Mahalakshmi, M. S., Sreekanth, M., Adinarayana, M., & Rao, Y. K. (2015). Efficacy of some novel insecticide molecules against incidence of whiteflies (Bemisia tabaci Genn.) and occurrence of Yellow Mosaic Virus (YMV) disease in urdbean. International Journal of Pure and Applied Bioscience, 3(5), 101-106.
Meghashree, M., & Mallikarjun, K. (2018). Influence of dates of sowing on incidence of Mungbean Yellow Mosaic Virus (MYMV) in mungbean. International Journal of Current Microbiology and Applied Sciences, 7(9), 2362- 2367
MOALD. (2022). Statistical Information on Nepalese Agriculture 2078/79(2021/22). Government of Nepal, Ministry of agriculture and livestock development, Planning and development cooperation coordination division, Statistics and analysis section, Singhdurbar, Kathmandu, Nepal.
Naeem, M., Farooq, M., Farooq, S., Ul-Allah, S., Alfarraj, S., & Hussain, M. (2021). The impact of different crop sequences on weed infestation and productivity of barley (Hordeum vulgare L.) under different tillage systems. Crop Protection, 149, 105759.
Naeem, M., Minhas, W. A., Hussain, S., Ul-Allah, S., Farooq, M., Farooq, S., & Hussain, M. (2022). Barley-based cropping systems and weed control strategies influence weed infestation, soil properties and barley productivity. Agriculture, 12(4), 487.
Naveed, M., Shafiq, M., Rafiq, C. M., & Saeed, M. S. (2015). Planting date effects on the incidence of mungbean yellow mosaic virus (MYMV) and cultivars performance under rainfed environments. Plant Knowledge Journal, 4(1), 7-12.
Parihar, A. K., Kumar, A., Dixit, G. P., & Gupta, S. (2017). Seasonal effects on outbreak of yellow mosaic disease in released cultivars of mungbean (Vigna radiata) and urdbean (Vigna mungo). Indian Journal of Agricultural Science, 87(6), 734-738.
Prasad, C. R., Prasad, K. V. H., Panduranga, G. S., & Kumar, A. R. N. (2022). Seasonal incidence of whitefly, Bemisia tabaci (Gennadius) and yellow mosaic disease (YMD) on blackgram in Southern zone of Andhra Pradesh. The Pharma Innovation Journal, 11(12), 2459-2464
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2022 Agriculture and Environmental Science Academy

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.




