Responses of potato to different methods of zinc and boron application in midhills of Nepal
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.26832/24566632.2024.0904024Keywords:
Agriculture lime boron, Foliar application, Micronutrients, Potato tuber yieldAbstract
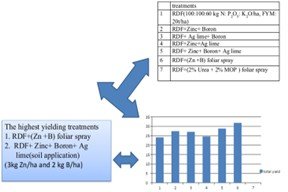
Zinc (Zn) and boron (B) are important micronutrients for potato production and they play a critical role to achieve the potential yield. This research was conducted to evaluate the effects of the foliar and soil application of Zn, B, and agriculture lime in enhancing potato (cv. Khumal Bikash) yield and size of tuber. The experiment was conducted for two consecutive years (2022 and 2023) at the National Potato Research Program, Khumaltar, Nepal. Seven fertilizer treatments, namely T1: recommended dose of NPK (RDF); T2: RDF+ Zn+ B; T3: RDF +B +Ag-lime; T4: RDF +Zn +Ag-lime; T5: RDF +Zn +B +Ag-Lime; T6: RDF +(Z +B) foliar Spray; T7: RDF + foliar Spray (2% urea +2% K) were arranged in a randomized complete block design. Foliar spray was applied twice, once at 40 DAP and again after 60 DAP. Ag-lime was applied before 15 DAP. Among seven treatments, T6 (RDF +Zn +B foliar spray) showed a significant effect on yield (31.84 t/ha) and its variables including vigor, uniformity and ground cover of potato followed by T5 (28.81 t/ha) and T7 compared to the treatments without Zn and B. Foliar application of mixture of Zn and B (3 kg Zn/ha + 2 kg B/ha) significantly improved germination, vigor, sizes and number of tuber and total yield compared to a separate application of Zn or B. The treatment T6 (RDF + Zn + B foliar) demonstrated the highest micronutrient efficiency (1494 kg ) highlighting the superior effectiveness of foliar application compared to other treatments. These findings suggest that micronutrients Zn and B is important to increase potato tuber yield and maximum benefits could be achieved with the foliar application at 2 splits.
Downloads
References
Adhikari, S. P., Timsina, K. P., Ghimire, Y. N., Gairhe, S., Brown, P. R., & Villano, R. (2023). Analysis of technical efficiency and yield gap of potato farmers in Nepal. Journal of Nepal Agricultural Research Council, 47-60.
Ali, S., Javed, H. U., Rehman, R. N., Sabir, I. A, Naeem, M. S., &Siddiqui, M. Z. (2013). Foliar application of some macro and micro nutrients improves tomato growth, flowering and yield. International Journal of Bioscience, 3(10), 280–287.
Andersen, P. (2007). A review of micronutrient problems in the cultivated soil of Nepal. Mountain Research and Development, 27(4), 331-335.
Giri, R., Upadhyay, K., Bhusal, Y., Dhakal, R., Subedi, G., Chalise, B., & Poudel, B. (2023). Performance evaluation of nutrient dense potato genotypes at high hills of Karnali Province, Nepal. Asian Journal of Advances in Agricultural Research, 21, 1-15. https://doi.org/10.9734/ajaar/2023/v21i2415
Karki, K. B., Tuladhar, J., Uprety, R., & Maskey, S. L. (2004). Distribution of micronutrients available to plants in different ecological regions of Nepal. In Proceedings of an International Workshop on Micronutrients in Southeast Asia (pp. 17–29). Kathmandu, Nepal.
Kumar, K., & Kumar, M. (2020). Effect of foliar micronutrients application on potato cultivation. Just Agriculture, 1(3), 1.
Kumar, R., Kumar, B., Saren, B., & Patel, S. (2023). Effect of foliar application of zinc and boron on growth attributes and yield of chickpea (Cicer arietinum L.) varieties. International Journal of Plant & Soil Science, 35, 958-965. https://doi.org/10.9734/IJPSS/2023/v35i214066
Lenka, B., & Das, S. (2019). Effect of boron and zinc application on growth and productivity of potato (Solanum tuberosum) at alluvial soil (Entisols) of India. Indian Journal of Agronomy, 64, 129-137.
Ministry of Agriculture and Livestock Development. (2017). Statistical information on Nepalese agriculture 2073/74 (2016/17). Kathmandu: Ministry of Agriculture and Livestock Development.
National Potato Research Program. (2023). Annual report 2022/23. Nepal Agricultural Research Council, Khumaltar, Lalitpur, Nepal.
Pasala, R., Ramesh, K., Pandey, B. B., Manikanta, C. L. N., Gopika, K., Daniel, J., Elthury, S., & Yadav, P. (2021). Recent advances in micronutrient foliar spray for enhancing crop productivity and managing abiotic stress tolerance. In Advances in Agronomy, 169, 263-308. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-822916-3.00008-1
Shireen, F., Nawaz, M. A., Xiong, M., Ahmad, A., Sohail, H., & Chen, Z. (2020). Pumpkin rootstock improves the growth and development of watermelon by enhancing uptake and transport of boron and regulating the gene expression. Plant Physiology and Biochemistry, 154, 204-218. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plaphy.2020.06.017
Shrestha, S., Becker, M., Lamers, J. P., & Wimmer, M. A. (2020). Diagnosis of zinc and boron availability in emerging vegetable-based crop rotations in Nepal. Journal of Plant Nutrition and Soil Science, 183(4), 429-438.
Singh, N., & Kathayat, K. (2018). Integrated application of micronutrients to improve growth, yield, quality and economic yield in potato-A Review. International Journal of Current Microbiology and Applied Sciences, 7(8), 2930-2935.
Singh, P., & Singh, K. (2019). Role of micronutrients in potato cultivation. Journal of Pharmacognosy and Phytochemistry, 128-130
Tariq, M., Ahmad, B., Adnan, M., Mian, I. A., Khan, S., Fahad, S., & Ali, S. (2022). Improving boron use efficiency via different application techniques for optimum production of good quality potato (Solanum tuberosum L.) in alkaline soil. PloS One, 17(1), e0259403.
Trehan, S. P., & Grewal, J. S. 1989. Micronutrients management in potato. (In) Annual Report, Central Potato Research Station, Jalandhar, Punjab, pp. 106.
Tripathi, B. P., Timsina, J., Vista, S. P., Gaihre, Y. K., & Sapkota, B. R. (2022). Improving soil health and soil security for food and nutrition security in Nepal. In J. Timsina, T. N. Maraseni, D. Gauchan, J. Adhikari, & H. Ojha (Eds.), Agriculture, natural resources and food security (Sustainable Development Goals Series). Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-09555-9_8
Uikey, S., Das, M.P., Ramgiry, P., Vijayvergiya, D., Ghaday, P., Ali, S & Pradhan, J. (2018). Effect of zinc, boron and iron on growth and phenological characters of brinjal (Solanum melongena L.). International Journal of Current Microbiology and Applied Sciences, 7, 1643-1649.
Yogi, L. N., Bhandari, S., Thalal, T., Bhattarai, M., Upadhyay, A., & Kharel, B. (2024). Enhancing rice yields through foliar application of essential micronutrients: A study on zinc, copper, and boron nutrition in context of Nepal. Archives of Agriculture and Environmental Science, 9(2), 373-78, https://dx.doi.org/10.26832/24566632.2024.0902024
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2024 Agriculture and Environmental Science Academy

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.




