Effects of various methods of milking, container types, and chilling durations on bacterial load of milk
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.26832/24566632.2024.090409Keywords:
Cow breed, Chilling duration, Milking methods, Standard Plate CountAbstract
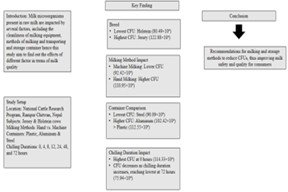
This study was carried out to evaluate the quality of raw milk measured by Standard Plate Count (SPC). Individual raw milk for the Colony Forming Units (CFU) study was carried out in the National Cattle Research Program Rampur Chitwan, Nepal. Milk from Jersey and Holstein cows with two types of milking (hand and machine milking) in collecting three types of containers (Plastic, aluminum, and steel). Milk had different chilling durations (0, 4, 8, 12, 24, 48, and 72 hours). Altogether, 252 milk samples for SPC were examined at farm levels. Results showed significant variability in SPC throughout the study period. The lowest CFU was observed in Holstein cows (80.49±4.83 × 104), while the highest was found in the Jersey breed (122.88±4.69 × 104). Similarly, the lowest CFU count was recorded in milk from machine milking (92.42±4.69 × 104), whereas the highest CFU count was observed in milk from hand milking (110.95±4.83 × 104). For three milk collecting and transporting containers, the CFU count was lowest in the steel container (90.09±5.82×104) compared to the aluminum container (102.42±5.82×104) and plastic container (112.55±5.82×104). The results of mean CFU for the chilling duration effects at farm 0, 4, 8,12,24,48 and 72 hours were (114.33±8.11×104, 108.21±10.28×104, 107.71±10.28×104, 106.75±10.28 ×104, 104.07±6.36 ×104, 94.79±8.11×104, and 75.94±8.11×104). CFU count in hand and machine milking milk differed significantly (p<0.01) from each record of the same date at the farm level. The CFU in milk from different containers was significant (p<0.05) for the overall experimental period. Steel containers showed a low CFU count compared to Aluminum and plastic containers. The highest number of CFU (114.33×104) was observed in the 0-hour chilling, which was significantly (p <0.05) different from the rest of the chilling duration. The results obtained from the study indicated that the current situation is critical and needs real improvement from farm to chilling centers. The findings could guide dairy producers in adopting effective strategies to enhance milk quality, minimize bacterial contamination, and ensure safer dairy products for consumers by using these results.
Downloads
References
Abakar, H. (2021). Effect of milking system on total bacterial count in cow raw milk. Afribary. Retrieved from https://afribary.com/works/effect-of-milking-system-on-total-bacterial-count-in-cow-raw-milk
Acharya, S., Bimali, N., Shrestha, S., & Lekhak B (2017). Bacterial Analysis of Different Types of Milk (Pasteurized, Unpasteurized and Raw Milk) Consumed in Kathmandu Valley. Tribhuvan University Journal of Microbiology, 4, 3-3
Al Juhaiman, L.A. (2010). Estimating Aluminum leaching from Aluminum cookware in different meat extracts and milk. Journal of Saudi Chemical Society, 14, 131-137.
Amagliani, G., Petruzzelli, A., Omiccioli, E., Tonucci, F., Magnani, M., & Brandi, G. (2012). Microbiological surveillance of a bovine raw milk farm through multiplex real-time PCR. Foodborne Pathogens and Disease, 9, 406–411. https://doi.org/10.1089/fpd.2011.104
Berhanu, L., Gume, B., Kassa, T., Dadi, L. S., Tegegne, D., Getnet, M., Bediru, H., Getaneh, A., Suleman, S., Mereta, S. T. (2021). Microbial quality of raw cow milk and its predictors along the dairy value chain in Southwest Ethiopia. International Journal of Food Microbiology, 350, 109228.
Bureau of Indian Standards, (1992). SP: 18. ISI Hand Book of Food Analysis. Part I. Bureau of Indian Standards, New Delhi.
Boor, K. J., Brown, D. P., Murphy, S. C., Kozlowski, S. M., & Bandler, D. K. (1998). Microbiological and chemical quality of raw milk in New York State. Journal of Dairy Science, 81(6), 1743-1748.
Calgaro, J., Dileta, A., Júnior, F., Marcos, P., João, V., Carol, T., Fernanda, S., & Ione, H.V. (2020). Production and composition of milk per Holstein and Jersey cow from two farms in northwest Rio Grande do Sul. Revista Brasileira de Saude e Producao Animal, 21. https://doi.org/10.1590/S1519-9940212121202
Chen, H., Lee, P., & Tu, Y. (2014). Bacterial attachment to different materials in dairy processing plants. International Dairy Journal, 39(1), 1-9.
Cremonesi, P., Morandi, S., Ceccarani, C., Battelli, G., Castiglioni, B., Cologna, N., Goss, A., Severgnini, M., Mazzucchi, M., Partel, E. (2020). Raw Milk Microbiota Modifications as Affected by Chlorine Usage for Cleaning Procedures: The Trentingrana PDO Case. Frontiers in Microbiology, 11, 564749.
Czerniewicz, M., Kiełczewska, K., Kruk, A. (2006). Comparison of some physicochemical properties of milk from Holstein-Friesian and Jersey cows. Polish Journal of Food and Nutrition Sciences, 56(1s), 61-64.
Dahal, L. R., Karki, D. B. N., & Shah, R. (2010). Total bacterial counts of raw milk in Eastern Terai of Nepal. Journal of Agriculture and Environment, 11, 46-50
Deeb, A. M. M. & Gomaa, G. M. (2011). Detection of aluminum in some dairy products at Kafr El-Sheikh, Egypt. Global Veterinary, 6: 1-5.
De Vliegher, S., et al. (2005). Differences in immune responses between dairy cows and their effect on udder health. Veterinary Research, 36(5-6), 703-717.
DeVries, A., & Putnam, L. (2019). Milking practices and their effect on bacterial contamination in milk: A comparative study of hand and machine milking. Dairy Science & Technology, 99(2), 145-157.
FAO (2022) Retrieved from www.openknowledge.fao.org/server/api/core/bitstreams/603a4a27-dea5-4654-9ee0-2507dddcaf02/content on November 10, 2024
Elmoslemany, A. M., et al. (2010). Incidence and Distribution of Bacterial Contamination in Raw Milk." Journal of Dairy Science, 93(11), 5281-5290.
FAO & IDF. (2011). Guide to good dairy farming practice. Animal Production and Health Guidelines. No. 8. Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO) and the International Dairy Federation (IDF), Rome.
Filipovic, D., & Kokaj, M. (2009). The comparison of hand and machine milking on small family dairy farms in central Croatia. Livestock Research for Rural Development, 21.
Fox, P. F., Uniacke-Lowe, T., McSweeney, P. L. H., & O'Mahony, J. A. (2017). Dairy Chemistry and Biochemistry. Springer.
Gleeson, D., O'Connell, A., & Jordan, K. (2013). Review of potential sources and control of thermoduric bacteria in bulk-tank milk. Irish Journal of Agricultural and Food Research, 52(2), 217-227.
Gouranga, C. C. (2008). Microbiological profile of the traditionally collected industrial raw milk from the milk pocket zones of Bangladesh. Bangladesh Journal of Microbiology, 25,17-20.
Gume, B., Berhanu, L., Kassa, T., Bediru, H., Fikre, A. G., Dadi, L. S. & Mereta, S., T. (2023). Bacterial hazard identification and exposure assessment of raw milk consumption in Jimma zone, South West Ethiopia. BMC Microbiology, 23(166). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12866-023-02910-0
Gurunathan (2023). Evaluation of quality and shelf-life of yak milk phrum during refrigerated storage. Milk Science International-Milchwissenschaft, 76(2).
Gunasena, D., & Siriwardhana, B. (2021). Evaluation of microbiological and compositional quality of raw cow’s milk (Household and Bulk) in Lankapura, Polonnaruwa, Sri Lanka. European Journal of Agriculture and Food Sciences, 3, 166-175. https://doi.org/10.24018/ejfood.2021.3.1.249
Jang, W. J., & Lee, J. S. (2020). Effect of container material on the quality and shelf-life of refrigerated milk. Food Control, 112, 107-112.
Jayarao, B. M., & Henning, D. R. (2001). Prevalence of Foodborne Pathogens in Bulk Tank Milk. Journal of Dairy Science, 84(10), 2157-2162.
Lejeune, J. T., & Rajala-Schultz, P. J. (2009). Food safety: Unpasteurized milk: A continued public health threat. Clinical Infectious Diseases, 48(1), 93-100.
Li, N., Wang, Y., You, C., Ren, J., Chen, W., Zheng, H., Liu, Z. (2018). Variation in Raw Milk Microbiota throughout 12 Months and the Impact of Weather Conditions. Scientific Report, 8, 2371.
Lore, T. A., Kurwijila, L. R., & Omore, A. (2006) Hygienic milk production: A training guide for farm-level workers and milk handlers in Eastern Africa. Module 1 Kenya.
Machado, S.G., Baglinière, F., Marchand, S., Van Coillie, E., Vanetti, M.C.D., De Block, J., & Heyndrickx, M. (2017). The biodiversity of the microbiota producing heat-resistant enzymes responsible for spoilage in processed bovine milk and dairy products. Frontiers in Microbiology, 8, 302.
MOAD. (2016). Report on Dairy Value Chain Round Table Meeting. Ministry of Agricultural Development (MOAD), Project for Agriculture Commercialization and Trade (PACT), Kathmandu.
Naing, Y. W., Wai, S. S., Lin, T. N., Thu, W. P., Htun, L. L., Bawm, S., & Myaing, T. T. (2019). Bacterial content and associated risk factors influencing the quality of bulk tank milk collected from dairy cattle farms in Mandalay Region. Food Science and Nutrition, 7, 1063–1071.
Nyokabia, S., Luning, P. A., de Boera, I. J. M., Korird, L., Muundad, E., Bebec, B. O., Lindahle, J., Bettd, B. & Oostinga, S. J. (2021). Milk quality and hygiene: Knowledge, attitudes and practices of smallholder dairy farmers in central Kenya. Food Control, 130, 108303. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodcont.2021.108303
Owusu-Kwarteng, J., Fortune, A., Dominic, A., & Lene, J. (2020). Microorganisms microbial safety of milk production and fermented dairy products in Africa. Microorganisms, 8. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms8050752
O'Brien, B., Berry, D. P., Kelly, A., & Meaney, W. J. (2016). The effect of breed on the quality of milk. Animal Science Journal, 87(8), 1035-1043.
Oie, S., & Kamiya, A. (2001). Comparison of microbial contamination of enteral feeding solution between repeated use of administration sets after washing with water and after washing followed by disinfection. Journal of Hospital Infection, 48, 304-307.
Parente, E., Ricciardi, A., Zotta, T. (2020). The microbiota of dairy milk: A review. International Dairy Journal, 107, 104714.
Peterková, L. (2002). Free fatty acids ratio in milk, factors which affect their concentration and possibilities their determination, pp. 26–30.
Petróczki, F., Andualem, T., Béla, B., & Ferenc, P. (2019). The effect of breed and stage of lactation on the microbiological status of raw milk. Acta Agraria Debreceniensis, 37-45. https://doi.org/10.34101/actaagrar/1/2367
Phattepuri, S., Subba, P., Ghimire, A. & Sah, S. N. (2020). Antibiogram Profiling and Thermal Inactivation OF Staphylococcus aureus and Escherichia coli Isolated from Milk of Dharan Nepal. Himalayan Journal of Science and Technology, 81-87.
Ranjit, D., Adhikari, R.P., Regmi, S. & Shah, P.K. (2008). Quality Survey of raw milk samples in eastern Nepal: A microbiological assessment in milk chain system. Journal of Nepal Health Research Council, 1(1), 17-21
Reche, N. L. M., Thaler Neto, A., D’Ovidio, L., Felipus, N. C., Pereira, L. C., Cardozo, L. L., Picinin, L. C. A. (2015). Multiplicação microbiana no leite cru armazenado em tanques de expansão direta. Ciência Rural, 45(5), 828-834. https://doi.org/10.1590/0103-8478cr20140542
Ruegg, P. L. (2003a). The impact of milking practices on the quality of milk: A review. Veterinary Clinics of North America: Food Animal Practice, 19(1), 39-62.
Ruegg, P. L. (2003b). Practical food safety interventions for dairy production. Journal of Dairy Science, 86(E. Suppl.), E1-E9.
Semwal, A. D., A. Padmashree, M. A. Khan, G. K. Sharma and A. S. Bawa, 2006. Leaching of aluminium from utensils during cooking of food. Journal of the Science of Food and Agriculture, 86, 2425-2430.
Shija, F. (2013). Assessment of milk handling practices and bacterial contaminations along the dairy value chain in Lushoto and Handeni districts in Tanga region. Morogoro, Tanzania, MSc Thesis : Sokoine University of Agriculture.
Skeie, S.B., Håland, M., Thorsen, I.M., Narvhus, J., Porcellato, D. (2019). Bulk tank raw milk microbiota differs within and between farms: A moving goalpost challenging quality control. Journal of Dairy Science, 102, 1959–1971.
Smith, G. C., & Jones, A. A. (2018). The effect of breed on milk composition and bacterial growth during storage. Journal of Dairy Research, 85(4), 523-531.
Soyeurt, H., Dardenne, P., Gillon, A., Croquet, C., Vanderick, S., Mayeres, P., & Gengler, N. (2006). Variation in fatty acid contents of milk and milk fat within and across breeds. Journal of Dairy Science, 89(12), 4858-4865.
Stefan, G., & Baraitareanu, S. (2024). Approaches of Milking Biosecurity and Milking Parlour Hygiene in Dairy Farms. IntechOpen. https://doi.org/10.5772/intechopen.113084
Swai, E., & Schoonman, L. (2011). Microbial quality and associated health risks of raw milk marketed in Tanga Region of Tanzania. Asian Pacific Journal of Tropical Biomedicine, 1(3), 217-222
Tadesse, A., Galmessa, U., & Bekuma, A. (2020). Milk Handling, Processing Practices and Quality Evaluation. Global Journal of Animal Scientific Research, 8(1), 56-74. Retrieved from http://www.gjasr.com/index.php/GJASR/article/view/34
Tiwari, U., & Paudel, K.P. (2018). Behavioral practices of supply chain actors on quality maintenance of raw milk in Nepal. Journal of Agriculture and Forestry University, 2, 79-89
Wafula, W.N., Matofari, W.J., & Nduko, M.J. et al. (2016). Effectiveness of the sanitation regimes used by dairy actors to control microbial contamination of plastic jerry cans’ surfaces. Food Contamination, 3, 9 https://doi.org/10.1186/s40550-016-0032-8
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2024 Agriculture and Environmental Science Academy

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.




