Suitability of groundwater quality for irrigation in and around the main Gadilam river basin on the east coast of southern India
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.26832/24566632.2020.0504019Keywords:
Groundwater, Irrigation water quality, Main Gadilam River basin, South IndiaAbstract
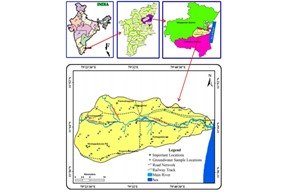
The main intent of this study was to investigate the condition of groundwater quality for irrigation purposes in and around the main Gadilam river basin, the east coast of southern India. A total of fifty groundwater samples were collected and analyzed for various parameters such as electrical conductivity (EC), pH, TDS, major cations (Ca2+, Mg2+, Na+, and K+) and anions (SO42-, Cl-, HCO3-, and NO3-). Irrigation water quality parameters like the sodium absorption ratio (SAR), residual sodium carbonate (RSC), percentage sodium (%Na), magnesium hazard (MH), permeability index (PI), and Kelly ratio (KR) were computed to assess the irrigation water quality of groundwater. Furthermore, graphical representation diagrams such as USSL, Wilcox, and Doneen have been prepared for irrigation water quality. From the computation of SAR, Na%, RSC, PI, and KR values, it was found that 100% of groundwater samples were found to be suitable for irrigation purposes. Besides, USSL and Doneen diagrams show that the samples are safe for irrigation usage. The Wilcox diagram in the classification of electrical conductivity reveals that most samples fall into the good to permissible class (78%), in doubtful to unsuitable class (20%), and 2% of samples are unsuitable. Magnesium hazards of 82% of the groundwater samples are suitable for irrigation, while the remaining 18% of the samples exceeded the limit and found to be unsuitable for irrigation purposes. The study concludes that higher percentages of groundwater samples were suitable for irrigation purposes in the study area, and the concentration of magnesium influenced groundwater at a few locations.
Downloads
References
Adimalla, N. (2019). Groundwater quality for drinking and irrigation purposes and potential health risks assessment: a case study from semi-arid region of South India. Exposure and Health, 11(2): 109-123, https://doi.org/10.1007/s12403-018-0288-8
Ahada, C.P.S. and Suthar, S. (2018). Assessing groundwater hydrochemistry of Malwa Punjab, India. Arabian Journal of Geosciences, 11: 17, https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-017-3355-8
Amiri, V., Sohrabi, N. and Dadgar, M.A. (2015). Evaluation of groundwater chemistry and its suitability for drinking and agricultural uses in the Lenjanat plain, Central Iran. Environmental Earth Sciences, 74: 6163–6176, https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-015-4638-6
APHA (2012). Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater, 22nd edition. American Public Health Association, Washington, DC, USA.
Aravindan, S., Manivel, M., Rajendran, S., Bhuvaneshwari and Shankar, K. (2008). Groundwater Investigations in the hard rock region of gadilam river basin, Tamil Nadu. Journal of Eco-chronicle, 3(1): 21-30.
Aravindan, S., Shankar, K., Poovalinga Ganesh, B. and Dharani Rajan, K. (2010). Groundwater Geochemical mapping of in the hard rock area of Gadilam River basin, using GIS technique, Tamil Nadu. Indian Journal of Applied Geochemistry, 12(2): 209-216.
Aravindan, S. and Shankar, K. (2011). Ground Water Quality Maps of Paravanar River Sub Basin, Cuddalore District, Tamil Nadu, India. Journal of Indian Society of Remote Sensing, 39(4): 565–58, https://doi.org/10.1007/s12524-011-0152-9
Aravindan, S., Shankar, K. and Mini, S. S. (2011). Integrated Geohydrological Studies in the Sedimentary Part of Gadilam River Basin, Cuddalore District, Tamil Nadu. Asian Journal of Earth Sciences, 4: 183-192, https://doi.org/10.3923/ajes.2011.183.192
Aravinthasamy, P., Karunanidhi, D. and Subba Rao, N. (2020). Irrigation risk assessment of groundwater in a non-perennial river basin of South India: implication from irrigation water quality index (IWQI) and geographical information system (GIS) approaches. Arabian Journal of Geosciences, 13: 1125,https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-020-06103-1
Ayers, R.S, Westcott, D.W. (1985). Water quality for agriculture (No. 29): food and agriculture Organization of the United Nations, Rome, Italy.
Balamurugan, P., Kumar, P.S. and Shankar, K. (2020a). Dataset on the suitability of groundwater for drinking and irrigation purposes in the Sarabanga River region, Tamil Nadu, India, Data in Brief, 29: 105255, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dib.2020.105255
Balamurugan, P., Kumar, P.S., Shankar, K., Nagavinothini, R, Sajil Kumar, P.J. (2020c). Impact of climate and anthropogenic activities on groundwater quality for domestic and irrigation purposes in Attur region, Tamilnadu, India. Desalination and water treatment 208: 172-195, https://doi.org/10.5004/dwt.2020.26452
Balamurugan, P., Kumar, P.S., Shankar, K., Nagavinothini, R. and Vijayasurya, K. (2020b). Non-carcinogenic risk assessment of groundwater in southern part of Salem District in Tamilnadu, India. Journal of the Chilean Chemical Society, 65(1): 4697-4707, http://dx.doi.org/10.4067/S0717-97072020000104697
Bian, J., Nie, S., Wang, R., Wan, H. and Liu, C. (2018) Hydrochemical characteristics and quality assessment of groundwater for irrigation use in central and eastern Songnen plain, Northeast China. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 190(7): 1–16, https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-018-6774-4.
BIS (2012) Bureau of Indian standard specification for drinking water. IS: 10500, pp 1–5.
Doneen, L.D. (1964). Notes on water quality in agriculture. Department of Water Science and Engineering, University of California, Davis.
Esmeray, E. and Gökcekli, C. (2020). Assessment of groundwater quality for drinking and irrigation purposes in Karabuk province, Turkey. Environmental Earth Sciences, 79(13), 1-17, https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-020-09074-4
FAO, Food and Agriculture Organization (2006). Prospects for food, nutrition, agriculture, and major commodity groups. World agriculture: toward 2030–2050, Interim report. Global Perspective Studies Unit. FAO, Rome.
Handa, B.K. (1969). Description and classification of media for hydrogeochemical investigations. In: Symposium on ground water studies in arid and semiarid regions, Roorkee.
Javed, S.A. and Ullah, S. (2017) Spatial assessment of water quality parameters in Jhelum city (Pakistan). Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 189(119):1–16, https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-017-5822-9
Kavitha, M.T., Divahar, R., Meenambal, T., Shankar, K., Vijay Singh, R., Tamirat Dessalegn Haile and Chimdi Gadafa (2019a). Dataset on the assessment of water quality of surface water in Kalingarayan Canal for heavy metal pollution, Tamil Nadu. Data in Brief, 22: 878–884, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dib.2019.01.010
Kavitha, M.T., Shankar, K., Divahar, R., Meenambal, T. and Saravanan, R. (2019b). Impact of industrial wastewater disposal on surface water bodies in Kalingarayan canal, Erode district, Tamil Nadu, India. Archives of Agriculture and Environmental Science, 4(4): 379-387,
https://dx.doi.org/10.26832/24566632.2019.040403
Kawo, N.S. and Karuppannan, S. (2018). Groundwater quality assessment using water quality index and GIS technique in Modjo River Basin, central Ethiopia. Journal of African Earth Sciences, 147: 300-311, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jafrearsci.2018.06.034
Kelly, W.P. (1963). Use of Saline Irrigation Water. Soil Science, 95(4): 355-391.
Margat, J. and Van der Gun, J. (2013). Groundwater around the world. CRC Press/ Balkema, Leiden.
Marghade, D., Malpe, D.B. and Subba Rao, N. (2019). Applications of geochemical and multivariate statistical approaches for the evaluation of groundwater quality and human health risks in a semi arid region of eastern Maharashtra, India. Environmental Geochemistry Health, https://doi.org/10.1007/s10653-019-00478-1.
Palanisamy, A., Karunanidhi, D., Subramani, T. and Roy, P. D. (2020). Demarcation of groundwater quality domains using GIS for best agricultural practices in the drought-prone Shanmuganadhi River basin of South India. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-08518-5.
Panneerselvam, B, Paramasivam, S.K. and Karuppannan, S. (2020a). A GIS-based evaluation of hydrochemical characterisation of groundwater in hard rock region, South Tamil Nadu, India. Arabian Journal of Geosciences, 13(17): 1-22. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-020-05813-w
Panneerselvam, B., Karuppannan, S. and Muniraj, K. (2020b). Evaluation of drinking and irrigation suitability of groundwater with special emphasizing the health risk posed by nitrate contamination using nitrate pollution index (NPI) and human health risk assessment (HHRA). Human and Ecological Risk Assessment: An International Journal, 1–25, https://doi.org/10.1080/10807039.2020.1833300
Ravindra, K., Mor, S., Singh, A., Singh, V.J., Dhanda, N., Rani, P. and Mor, S. (2019). Hydro-chemistry of groundwater in a North Indian city and its suitability assessment for drinking and irrigation purposes. Journal of Environmental Biology, 40(2): 200-210, https://doi.org/10.22438/jeb/40/2/MRN-853
Rawat, K.S., Singh, S.K. and Gautam, S.K. (2018). Assessment of groundwater quality for irrigation use: a peninsular case study. Applied Water Science, 8(8): 233, https://doi.org/10.1007/s13201-018-0866-8
Richards, L.A. (1954). Diagnosis and Improvement of Saline and Alkali Soils Agriculture Handbook. 60, Department of Agricultural, Washington DC, US, pp- 160.
Saleh, A., Al-Ruwaih, F. and Shehata, M. (1999) Hydrogeochemical processes operating within the main aquifers of Kuwait. Journal of Arid Environment, 42: 195–209, https://doi.org/10.1006/jare.1999.0511
Shankar, K. and Kawo, N.S. (2019). Groundwater Quality Assessment Using Geospatial Techniques and WQI in North East of Adama Town, Oromia Region, Ethiopia. Hydrospatial Analysis, 3(1): 22-36, https://doi.org/10.21523/gcj3.19030103
Shankar, K., Aravindan, S. and Rajendran, S. (2010). GIS based groundwater quality mapping in Paravanar River Sub-Basin, Tamil Nadu, India. International Journal of Geomatics and Geosciences, 1(3): 282–296.
Shankar, K., Aravindan, S. and Rajendran, S. (2011) Hydrogeochemistry of the Paravanar River Sub-Basin, Cuddalore District, Tamilnadu, India. E-Journal of Chemistry, 8(2): 835-845, https://doi.org/10.1155/2011/107261.
Shankar, K., Aravindan, S. and Rajendran, S. (2011a) Hydrochemical profile for assessing the groundwater quality of Paravanar River Sub-Basin, Cuddalore district, Tamil Nadu, India. Current World Environment, 6(1): 45-52, http://dx.doi.org/10.12944/CWE.6.1.05
Shankar, K., Aravindan, S. and Rajendran, S. (2011b). Spatial distribution of groundwater quality in Paravanar river sub basin, Cuddalore district, Tamil Nadu. International Journal of Geomatics and Geosciences, 1(4): 914-931.
Shankar, K., Aravindan, S. and Rajendran, S. (2011c). Assessment of Ground Water Quality in Paravanar River Sub-Basin, Cuddalore district, Tamil Nadu, India. Advances in Applied Science Research, 2 (5): 92-103.
Solangi, G.S., Siyal, A.A., Babar, M.M. and Siyal, P. (2019). Application of water quality index, synthetic pollution index, and geospatial tools for the assessment of drinking water quality in the Indus Delta, Pakistan. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 191(12): 731, https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-019-7861-x
Soujanya Kamble, B., Saxena, P.R., Kurakalva, R.M. and Shankar.K. (2020). Evaluation of seasonal and temporal variations of groundwater quality around Jawaharnagar municipal solid waste dumpsite of Hyderabad city, India. SN Applied Sciences, 2: 498, https://doi.org/10.1007/s42452-020-2199-0
Todd, D.K. (1959). Groundwater hydrology, I edn. Willey, Hoboken, pp 336.
U. S. Salinity Laboratory (USSL) (1954). Diagnosis and improvement of saline and alkaline soil; USSA handbook No. 60 71.
Umamageswari, T.S.R, Sarala Thambavani, D. and Liviu, M. (2019). Hydrogeochemical processes in the groundwater environment of Batlagundu block, Dindigul district, Tamil Nadu: conventional graphical and multivariate statistical approach. Applied Water Science, 9(1):1–15, https://doi.org/10.1007/s13201-018-0890-8
Venkateswaran, S., Karuppannan, S. and Shankar, K. (2012). Groundwater Quality in Pambar Sub-Basin, Tamil Nadu, India Using GIS. International Journal of Recent Scientific Research, 3(10):782- 787.
Wagh, V.M., Panaskar, D.B., Varade, A.M., Mukate, S.V., Gaikwad, S.K., Pawar, R.S., Muley A.A. and Aamalawar, M.L. (2016). Major ion chemistry and quality assessment of the groundwater resources of Nanded tehsil, a part of southeast Deccan Volcanic Province, Maharashtra, India. Environmental Earth Sciences 75(21): 1418, https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-016-6212-2
Wagh, V., Panaskar, D. and Aamalawar, M. (2018). Hydro-chemical characterization and groundwater suitability for drinking and irrigation uses in semiarid region of Nashik, Maharashtra, India. Hydrospatial Analysis, 2: 43–60, https://doi.org/10.21523/gcj3.18020104
WHO (2011). World Health Organization Guidelines for Drinking Water Quality, 4rded. In: Incorporating the First and Second Addenda, 1Recommendation (Geneva).
Wilcox, L. (1955). Classification and use of irrigation waters (No. 969). US Department of Agriculture.
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2020 Agriculture and Environmental Science Academy

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.




