Appraisal of different doses of nitrogen fertilizer on growth and yield of eggplant (Solanum melongena L.)
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.26832/24566632.2020.050403Keywords:
Eggplant (Solanum melongena L.), Growth and yield, Nitrogenous fertilizer, UreaAbstract
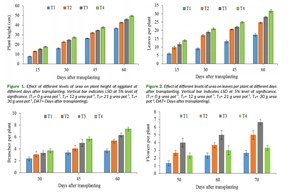
Nitrogenous fertilizer could improve the growth, yield and yield contributing characters of eggplant. The present investigation was aimed to find out the effects of different doses of nitrogen fertilizer on growth and yield of eggplant (Solanum melongena L.) which was conducted at Noakhali Science and Technology University during November, 2018 to March, 2019. The experiment comprises on eggplant local variety named ‘Tal begun’. There were four treatments of urea viz., 0, 12, 21 and 30 g urea pot-1 and the experiment were laid out in completely randomized design (CRD) with three replications. Different parameters were undertaken for the study like plant height (cm), number of leaves per plant, number of branches per plant, number of flowers per plant, number of fruits per plant, individual fruit weight (g). The variety showed significant variation for different doses. Among all treatments, 30 g urea pot-1 showed highest vegetative characteristics such as plant height (49.67 cm), number of leaves per plant (32.67), number of branches per plant (7.33) at 60 DAT and lowest vegetative characteristics was found from 0 g urea pot-1. On the other hand, the application of 21 g urea pot-1 showed medium vegetative characteristics and highest reproductive characteristics such as number of flowers per plant (6.67), number of fruits per plant (6.67), individual fruit weight (138.67 g). Therefore, the results showed that, nitrogen fertilizer strongly influenced vegetative and reproductive characteristics of eggplant. The findings of this study suggested that 21 g urea pot-1 performed the best and it will be suitable for eggplant production.
Downloads
References
Akanbi, W.B., Togun, A.O., Olaniran, O.A., Akinfasoye, J.O. and Tairu, F.M. (2007). Physico-chemical properties of eggplant (Solanum melongena L.) fruit in response to nitrogen fertilizer and fruit size. Agricultural Journal, 2(1): 140-148.
Aminifard, M.H., Aroiee, H., Fatemi, H., Ameri, A. and Karimpour, S. (2010). Responses of eggplant (Solanum melongena L.) to different rates of nitrogen under field conditions. Journal of Central European Agriculture, 11(4): 453-458.
Aujla, M.S., Thind, H.S. and Buttar, G.S. (2007). Fruit yield and water use efficiency of eggplant (Solanum melongema L.) as influenced by different quantities of nitrogen and water applied through drip and furrow irrigation. Scientia Horticulturae, 112(2): 142-148, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scienta.2006.12.020
Bar-Tal, A., Aloni, B., Karni, L. and Rosenberg, R. (2001). Nitrogen nutrition of greenhouse pepper: Effects of nitrogen concentration and NO3:NH4 ratio on growth, transpiration, and nutrient uptake. Horticultural Science, 36(7): 1252-1259, https://doi.org/10.21273/HORTSCI.36.7.1252
BBS (Bangladesh Bureau of Statistics) (2018). Yearbook of Agricultural Statistics-2017. 29th Series. Statistics and Informatics Division, Ministry of Planning, Government of the People’s Republic of Bangladesh. www.bbs.gov.bd
Begum, K., Mohiuddin, K.M., Zakir, H.M., Rahman, M.M. and Hasan, M.N. (2014). Heavy metal pollution and major nutrient elements assessment in the soils of Bogra city in Bangladesh. Canadian Chemical Transaction, 2(3): 316-326, https://doi.org/10.13179/canchemtrans.2014.02.03.0088
De Pascale, S., Tamburrino, R., Maggio, A., Barbieri, G., Fogliano, B. and Pernice, R. (2006). Effect of nitrogen fertilization on the nutritional value of organically and conventionally grown tomatoes. Acta Horticulturae, 700: 107-110, https://doi.org/10.17660/ActaHortic.2006.700.14
Devi, H.H., Maity, T.K., Paria, N.C. and Thapa, U. (2002). Response of brinjal to different sources of nitrogen. Journal of Vegetable Sciences, 29(1): 45-47.
Ge, T., Song, S., Chi, M., Huang, D. and Iwasaki, K. (2008). Effects of nitrogen forms on carbon and nitrogen accumulation in tomato seedling. Agricultural Sciences in China, 7(11): 1308-1317, https://doi.org/10.1016/S1671-2927(08)60179-0
Giannakoula, A., Moustakas, M., Syros, T. and Yupsanis, T. (2010). Aluminum stress induces up-regulation of an efficient antioxidant system in the Al-tolerant maize line but not in the Al- sensitive line. Environmental and Experimental Botany, 67(3): 487-494, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envexpbot.2009.07.010
Hussain, M.J., Ali, M.Y., Rahman, M.M., Quayyum, M.A. and Choudhury, D.A. (2010). Brinjal fruit yield in response to urea super granule application. The Agriculturists, 7(1): 6-11, https://doi.org/10.3329/agric.v7i1.5246
Jilani, M.S., Faheem, M.F. and Waseem, K. (2008). Effect of different nitrogen levels on growth and yield of brinjal (Solanum melongena L.). Journal of Agricultural Research, 46(3): 245-251.
Michalojc, Z. and Buczkowska, H. (2008). Content of macroelements in eggplant fruits depending on nitrogen fertilization and plant training method. Journal of Elementology, 13(2): 269-274.
Mirdad, Z.M. (2011). Vegetative growth yield and yield components of eggplant (Solanum melongena L.) as influenced by irrigation intervals and nitrogen levels. JKAU: Meteorology, Environment and Arid Land Agriculture Sciences, 22(1): 31-49, https://doi.org/10.4197/Met.22-1.3
Mohammad, H.A., Hossein, A., Hamide, F., Atefe, A. and Sajede, K. (2010). Responses of eggplant (Solanum melongena L.) to different rates of nitrogen under field conditions. Journal of Central European Agriculture, 11(4): 453-458.
Prabhu, M., Veeraragavathatham, D. and Srinivasa, K. (2003). Effect of nitrogen and phosphorous on growth and yield of brinjal. South Indian Horticulture, 51: 152-156.
Rosati A., Escobar G.A.J., Burns I.G., Booji R. and Neeteson J. (2002). First attempt to simulate the response of aubergine crops to N supply: a mean to optimize N fertilization. Acta Horticulturae, 571: 137-142, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jfca.2008.03.006
Sharmin, S. and Rahman, L. (2019). Optimization of nitrogen requirement for better growth and yield of brinjal (Solanum melongena L.). Archives of Agriculture and Environmental Science, 4(1): 33-38, https://doi.org/10.26832/24566632.2019.040105
Singh S.S., Gupta P. and Gupta A.K., (2003). Handbook of Agricultural Sciences. Kalyani Publishers, New Delhi, India. 184-185.
Souza, Á.H.C., Rezende, R., Lorenzoni, M.Z., Seron, C.C. and Santos, F.A.S. (2018). Agronomic efficiency and growth of eggplant crop under different potassium and nitrogen doses. Revista Caatinga, 31(3): 737-747, https://dx.doi.org/10.1590/1983-21252018v31n324rc
Ullio, L. (2003). Eggplant Growing. Agfact H8.1.29, 3rd Edition. NSW Agriculture, Australia. 1-4, www.agric.nsw.gov.au
Wange, S.S. and Kale, R.H. (2004). Effect of bio fertilizers and nitrogen levels on brinjal crop. Journal of Soils and Crops, 14(1): 9-11, https://doi.org/10.5897/AJB11.2450
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2020 Agriculture and Environmental Science Academy

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.




