Effects of industrial effluents on growth and heavy metals accumulation in cabbage in Bangladesh
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.26832/24566632.2022.070107Keywords:
Accumulation, Cabbage, Growth, Heavy metals, Industrial effluentsAbstract
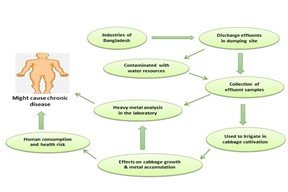
The purpose of this study was to assess the effects of industrial effluents on cabbage growth and heavy metal accumulation. Untreated effluents were collected from nine dumping sites in Bangladesh's Dhaka, Sylhet, and Chittagong divisions: including Narsingdi, Tongi, Hazaribagh, Alampur, Khadimnagar, Majortilla, Bhatiary, Bayazid bostami, and Sagorika. Pb (2.038 mgl-1), Cd (0.082 mgl-1), Ni (0.237 mgl-1) and Cr (0.172 mgl-1) concentrations found maximum in Hazaribagh effluents, whereas Fe (7.171 mgl-1) and Zn (1.938 mgl-1) were maximum in Khadimnagar. Two pot experiments were carried out in CRD with three replications. Untreated effluents had a significant influence on cabbage germination and growth in the early stages. Seed germination was reduced by 19.78% when Khadimnagar effluents were used instead of control. The seedling mortality rate in Khadimnagar effluents was higher (15.56 %), whereas no seedling mortality in the control. Because of the toxicity of heavy metals, shoot length (61.98%) and root length (66.76%), as well as other parameters, were lowered compared to control. The number of leaf plants-1, leaf length, leaf width, fresh weight, and dried weight were all highest in the control, while they were lowest when Khadimnagar effluents used as irrigation. The transfer factor values of several heavy metals (Pb-0.442, Cd-0.400, Ni-0.411, Cr-0.378, Fe-26.317, and Zn-22.951) were maximum when using effluents from Khadimnagar and Hazaribagh. Finally, the overall findings suggest that heavy metals including Pb, Cd, Ni, Cr, Fe, and Zn were significantly contaminated in Khadimnagar and Hazaribagh, with negative effects on cabbage growth and heavy metal accumulation in foodstuffs, potentially posing a health risk.
Downloads
References
Ahmed, G., Miah, M. A., Anawar, H. M., Chowdhury, D. A., & Ahmad, J. U. (2011). Influence of multi-industrial activities on trace metal contamination: an approach towards surface water body in the vicinity of Dhaka Export Processing Zone (DEPZ). Environmental Monitoring Assessment, 2(1), 1-10.
APHA (American Public Health Association). (2017). Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater. 23rd Edition, AWWA and WEF, Washington, USA. pp. 1-175.
Arora, M., Bala, K., Rani, S., Rani, A., Kaur, B., & Mittal, N. (2008). Heavy metal accumulation in vegetables irrigated with different water sources. Food Chemistry, 111(4), 811–815.
Ayers, R. S., & Westcot, D. W. (1985). Water quality for agriculture. FAO irrigation and drainage paper, 29, 8-96.
Bakali, B., Mia, M. Y., & Zakir, H. M. (2014). Water quality evaluation of tongi area in bangladesh: an impact of industrialization. Journal of Chemical, Biological and Physical Sciences, 4(2), 1735-1752.
Becerril, J., lez-Murua, C.Gl., Munoz-Rueda, A., & De Felipe, M. R. (1989). Changes induced by cadmium and lead in gas exchange and water relations of clover and lucerne. Plant Physiology and Biochemistry, 27(6), 913−918.
Chaves, L. H. G., Estrela, M. A., & Souza, R. S. (2011). Effect on plant growth and heavy metal accumulation by sunflower. Journal of Phytology, 3(12), 04-09.
Crichton, R. R., Wilmet, S., Legssyer, R., & Ward, R. J. (2002). Molecular and cellular mechanisms of iron homeostasis and toxicity in mammalian cells. Journal of Inorganic Biochemistry, 91(1), 9-18.
Cui, Y. J., Zhu, Y.G., Zhai, R. H., Chen, D. Y., Huang, Y.Z., Qiu, Y., & Ling, J.Z. (2004). Transfer of metals from soil to vegetables in an area near a smelter in Nanning, China. Environment International, 30(6), 785-791.
Datta, J.K., Bandhyopadhyay, A., Banerjee, A., & Mondal N. K. (2011). Phytotoxic effect of chromium on the germination, seedling growth of some wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) cultivars under laboratory condition. International Journal of Agricultural Technology, 7(2), 395−402.
DOE (Department of Environment). (2015). Bangladesh: State of the Environment. Ministry of Environment and Forestry. Publication, UNEP, pp. 1-74.
Hoagland, D. R. and Arnon, D. I. (1950). California Agricultural Experiment Station Circular, 347, 1-32.
Jadoon, I. B. K., Shafaqat, A., Qurratulain, B. K. J., Shako, M. B., Bharwana, S. A., & Farooq, M. A. (2013). Effects of irrigation with wastewater from different industries on vegetables grown in vicinity of Faisalabad, Pakistan. International Research Journal of Plant Science, 4(6), 144-148.
Juwarkar, A. S., & Shende, G. B. (1986). Interaction of Cd-Pb effect on growth yield and content of Cd, Pb in barley. Indian Journal of Environmental Health, 28, 235–243.
Kevresan, S., Petrovic, N., Popovic, M., & Kandrac, J. (2001). Nitrogen and protein metabolism in young pea plants as affected by different concentrations of nickel, cadmium, lead, and molybdenum. Journal of Plant Nutrition, 24(10), 1633-1644.
Khaleel, R. I., Ismail, N., & Ibrahim, M. H. (2013). The impact of waste water treatments on seed germination and biochemical parameter of Abelmoschus esculentus L. Procedia-Social and Behavioral Sciences, 91, 453-460,https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sbspro.2013.08.443
Kohinoor B. K. M., Mohiuddin, H. M., Zakir, M., Rahman, M., & Hasan, M. N. (2014). Heavy Metal Pollution and Major Nutrient Elements Assessment in the Soils of Bogra City in Bangladesh. Canadian Chemical Transactions, 2(3), 316-326.
Kumar, N., Bauddh, K., Kumar, S., Dwivedi, N., Singh, D.P., & Barman, S.C. (2013a). Accumulation of metals in weed species grown on the soil contaminated with industrial waste and their phytoremediation potential. Ecological Engineering, 61, 491–495, https://doi.org/10.1016/J.ecoleng.2013.10.004
Kumar, N., Bauddh, K., Kumar, S., Dwivedi, N., Singh, D.P., & Barman, S.C. (2013b). Extractability and phytotoxicity of heavy metals present in petrochemical industry sludge. Clean Technology Environmental Policy, 15(6), 1033–1039, https:doi.org/10.1007/s10098-012-0559-1
Li, W., Khan, M.A., Yamaguchi, S., & Kamiya Y. (2005). Effects of heavy metals on seed germination and early seedling growth of Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Growth Regulation, 46(1), 45-50, https://doi.org/10.1007/s10725-005-6324-2.
Mathur N., Bhatnagar P., & Verma H. (2006). Genotoxicity of vegetables irrigated by industrial wastewater. Journal of Environmental Sciences, 18(5), 964–968. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1001-0742(06)60022-3
Maukeeb, A. R. M., Mondal, M. F., Saha, M., & Hasan, M. K. (2018). Effects of industrial effluents on seed germination and growth of radish. Journal of Sylhet Agricultural University, 5(1), 51-59.
Muchuweti, M., Birkett, J. W., Chinyanga, E., Zvauya, R., Scrimshaw, M. D. and Lester, J. N. (2006). Heavy metal contents of vegetables irrigated with mixture of wastewater and sewage sludge in Zimbabwe: implications for human health. Agroforestry Ecosystem & Environment, 112(1), 41–48, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agee.2005.04.028
Nagada, G.K., Diwan, A.M., & Ghole, V.S. (2006). Seed germination bioassays to assess toxicity of molasses fermentation based bulk drug industry effluent. Electronic Journal of Environmental, Agriculture and Food Chemistry, 5(6),1598-1603.
Naidu, R., Wong, M.H., & Nathanail, P. (2015). Bioavailability-the underlying basis for risk- based land management. Environmental Science and Pollution Research International, 22, 8775-8778, https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-015-4295-z
Naser, H. M., Shil, N. C., Mahmud, N. U., Rashid, M. H., & Hossain, K. M. (2009). Lead, cadmium and nickel contents of vegetables grown in industrially polluted and non-polluted areas of Bangladesh. Bangladesh Journal of Agricultural Research, 34(4), 545-554.
Nenova, V. (2006). Effect of iron supply on growth and photosystem II efficiency of pea plants. General and Applied Plant Physiology, Special issue; 81-90.
Olaleye, A. O., Tabi, F. O., Ogunkunle, A. O., Singh, B. N., & Sahrawat, K. L. (2001). Effect of toxic iron concentrations on the growth of lowland Rice. Journal of Plant Nutrition, 24(3), 441-457.
Rasafi, T., Nouri, M., Bouda, S., & Haddioui A. (2016). The effect of Cd, Zn and Fe on seed germination and early seedling growth of wheat and bean. Ekologia (Bratislava), 35 (3), 213-223.
Saravanamoorthy, M., & Ranjitha-Kumari, B. D. (2007). Effects of textile wastewater on morphophysiology and yield of two varieties of peanut (Arachis hypogea L.). Journal of Agricultural Technology, 3(2), 335-343.
Shafiq, M. Zafar, I.M., & Athar, M. (2008). Effect of lead and cadmium on germination and seedling growth of Leucaena leucocephala. Journal of Applied Sciences and Environmental Management, 12(2), 61-66.
Sinha, S., Gupta, A. K., & Bhatt, K. (2007). Uptake and translocation of metals in fenugreek grown on soil amended with tannery sludge: Involvement of antioxidants. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 67(2), 267–277.
Tandon, H. L. S. (1995). Methods of Analysis of Soils, Plants, Waters and Fertilizers. Fertilizer Development and Consultation Organization, New Delhi, India. pp. 87-92.
Uaboi-Egbenni, P. O., Okolie, P. N., Adejuyitan, O. E., Sobande, A. O., & Akinyemi, O. (2009). Effects of industrial effluents on the growth and anatomical structure of Abelmoschus esculentus (Okra). African Journal of Biotechnology, 8(14), 3251-3260.
Uzair, M., Ahmad, M., & Nazim, K. (2009). Effects of industrial waste on seed bank and growth of wild plants in Dhabeji area, Karachi, Pakistan. Pakistan Journal of Botany, 41(4), 1659–1665.
Verma, L., & Pandey, N. (2017). The Effect of Iron Toxicity on Seed Germination and Early Seedling Growth of Green Gram (Vigna radiata L. Wilczek). International Journal of Science and Research, 6(8), 1427-1430.
Vijayaragavan, M., Prabhahar, C., Sureshkumar, J., Natarajan, A., Vijayarengan, P., & Sharavanan, S. (2011. Soil irrigation effect of sugar mill effluent on changes of growth and biochemical contents of Raphanus sativus L. Current Botany, 2(7), 9-13.
Yousaf, I., Ali, S.M., & Yasmin, A. (2010). Germination and early growth response of glycine max. varieties in textile and paper industry effluents. Pakistan Journal of Botany, 42(6), 3857–3863.
Zakir, H.M., Hasan, M.N., Quadir, Q., Sharmin, F. S., & Ahmed, I. (2013). Cadmium and lead pollution in sediments of midstream of the river Karatoa in Bangladesh. International Journal of Engineering Sciences, 2(2), 34-42.
Zakir, H.M., Rahman, M.M., Rahman, A., Ahmed, I., & Hossain. M.A. (2012). Heavy metals and major ionic pollution assessment in waters of midstream of the river Karatoa in Bangladesh. Journal of Environmental Science and Natural Resources, 5(2), 149-160.
Zakir, H. M., Sultana, N., & Akter, M. (2014). Heavy Metal Contamination in Roadside Soils and Grasses: A Case Study from Dhaka City, Bangladesh. Journal of Chemical, Biological and Physical Sciences, 4(2), 1661-1673.
Zheng, N., Wang, Q., Zhang, X., Zheng, D., Zhang, Z., & Znang, S. (2007). Population health risk due to dietary intake of heavy metals in the industrial area of Huludao City, China. Science of the Total Environment, 387(1-3), 96–104. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2007.07.044
Zurera, G., Estrada, B., Rincon, F., & Pozo, R. (1987.) Lead and cadmium contamination levels in edible vegetables. Bulletin of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 38(5), 805-812, https://doi.org/10.1007/B F01616705
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2022 Agriculture and Environmental Science Academy

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.




