Performance and supply chain analysis of Binalebu-1 in some selected areas of Bangladesh
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.26832/24566632.2022.070406Keywords:
Lemon, Profitability, BCR, Channel, Binalebu-1, Supply chainAbstract
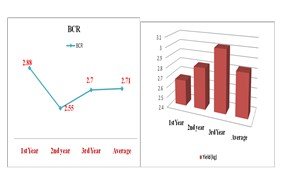
The study was conducted to find out the performance and supply chain of Binalebu-1 in four major Binalebu-1growing areas of Bangladesh, namely Cumilla, Mymensingh, Rangpur and Dhaka districts. Simple random sampling technique was followed for this study. The average cost of lemon production was estimated at Tk. 206127 per hectare of which about 68% was variable cost and 32% was fixed cost. Human labour cost was the lion share (32%) of total cost and it followed by irrigation cost (6.63%), Insecticide (2.64%) sapling (2.60%), and in the study areas. The average yield of Binalebu-1 was recorded 28.32 t/ha in all study areas while it was highest in 3rd year (30.24 t/ha) followed by 2nd year (28.17 t/ha) and 1st year (26.58 t/ha). The average gross return, gross margin and net return of lemon were found to be Tk 744517.62/ha, Tk 454521.67/ha, and Tk 538390.75/ha, respectively. Average BCR was found to be 2.71 on the basis of total cost. Supply chain was classified into four types: Channel 1: Accounts for 40 % which was ranked as I; Channel II: Accounts for 20 % which was Ranked as II; Channel III: Accounts for 18 % which was Ranked as III, Channel IV: Accounts for 12 % which was ranked as IV; Channel V: Accounts for 10 % which was Ranked as V. It was revealed that the value addition of the Faria, Bepari, Paiker, Arathdar, Retailer were Tk.135, Tk.95, Tk.55, Tk.39 and, Tk155 per quintal, respectively.
Downloads
References
Ahmed, F., Zareen, M., Khan, M. R., Banu, C. P., Haq, M. N., & Jackson, A. A. (1998). Dietary pattern, nutrient intake and growth of adolescent school girls in urban Bangladesh. Public Health Nutrition, 1(2), 83-92.
Bony, Z. F., Rahman, M. A., Al Riyadh, Z., Saha, S. R., & Zakaria, M. (2021). Productivity and Profitability Assessment of Lemon Based Agroforestry Systems in Bangladesh. 14(2), 42-49
Bangladesh Institute of Nuclear Agriculture. Retrieved from http://bina.portal.gov.bd/ Accessed on 9 December, 2022
Dillon, J. J., & Hardaker, J. B. (1993). Farm Management Research for small Farmer development, Agricultural Services Bulletin, 41, FAO, Rome.
Hasan, S., Haque, M. E., Afrad, M. S. I., Alam, M. Z., Hoque, M. Z., & Islam, M. R. (2021a). Pest risk analysis and management practices for increasing profitability of lemon production. Journal of Agriculture and Ecology Research International, 22(1), 25-35.
Hasan, S., Haque, M. E., Afrad, M. S. I., Alam, M. Z., Hoque, M. Z., & Islam, M. R. (2021b). Influences of socio-economic factors on lemon pest management practices in Tangail district of Bangladesh. South Asian Journal of Social Studies and Economics, 10(3), 59-67.
Hels, O., Kidmose, U., Larsen, T., Hassan, N., Tetens, I., & Haraksingh Thilsted, S. (2003). Estimated nutrient intakes and adequacies in Bangladesh change when newer values for vitamin A, iron and calcium in commonly consumed foods are applied. International Journal of Food Sciences and Nutrition, 54(6), 457-465.
Julia F. Morton (1987). "Lemon in Fruits of Warm Climates". Purdue University. 160– 168
Khan, M. R., & Ahmed, F. (2005). Physical status, nutrient intake and dietary pattern of adolescent female factory workers in urban Bangladesh. Asia Pacific Journal of Clinical Nutrition, 14(1), 19.
Sfgate (2017). Do Lemons Provide Vitamin C Like Oranges Do? http://healthyeating.sfgate.com/lemonsprovide-vitamin-c-like-oranges-do-3508.html, access on April 9, 2017.
Ismail, M., & Zhang, J. (2004). Post-harvest citrus diseases and their control. Outlooks on Pest Management, 15(1), 29-35.
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2022 Agriculture and Environmental Science Academy

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.




