Efficacy of eco-friendly insecticides against yellow stem borer under spring rice crop ecosystem of Saptari district, Nepal
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.26832/24566632.2023.080203Keywords:
Bacillus thuringiensis, Eco-friendly insecticides, Neembicide, Scirpophaga incertulas, Yellow stem borerAbstract
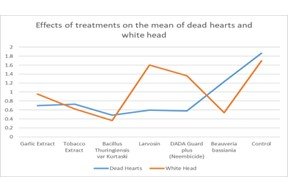
The study aimed to assess the effectiveness of eco-friendly insecticides in controlling yellow stem borer in spring rice crops of Hardinath-1 variety in Saptari district, Nepal. For this experiment, a Randomized Block Design was used with seven different treatments and an untreated control group. The treatments tested included Bacillus thuringiensis var kurtaski, Beauveria bassiana, Azadiractin 2.00%, garlic extract, tobacco extract, larvosin, and an untreated plot. The plots used were 3 × 4 meters in size and the plants were spaced 20 centimeters apart in both rows and between plants. The crop was sprayed twice, once during the vegetative stage and once during the reproductive stage, when the pest population reached a certain level. The incidence of dead heart was observed on ten randomly selected hills from each plot before and after the insecticide application, and observations on yellow stem borer incidence were recorded. Results showed that B. thuringiensis var kurtaski had the lowest dead heart infestation (0.4889%) and the minimum white head infestation (0.367%), as well as the highest mean yield (5.755mt/ha). Neembicide and B. bassiana also showed promising results.
Downloads
References
Balasubramamiam, M., & Kumar, K. (2019). Bioefficacy of neem formulations against the rice yellow stem borer, S. incertulas (Walk.). 7(3), 1145–1149.
Chatterjee, S., & Mondal, P. (2014) Management of rice yellow stem borer, Scirpophaga incertulas Walker using some biorational insecticides. Management of rice yellow stem borer, Journal of Biopesticides 7, 143-147.
Estiati, A. (2020). Development of Bt rice potential for yellow stem borer control. Journal of Crop Science and Biotechnology, 23(5), 395–403, https://doi.org/10.1007/s12892-020-00025-w
Hashemitassuji, A., Safaralizadeh, M. H., Aramideh, S., & Hashemitassuji, Z. (2015). Effects of Bacillus thuringiensis var. kurstaki and Spinosad on three larval stages 1st, 2nd and 3rd of tomato borer, Tuta absoluta (Meyrick) (Lepidoptera: Gelechiidae) in laboratory conditions. Archives of Phytopathology and Plant Protection, 48(5), 377–384, https://doi.org/10.1080/03235408.2014.893630
IRRI (2019). http://books.irri.org/AR2019_content.pdf
Khosla, R. K. (1977). Techniques for assessment of losses due to pests and diseases of rice. Indian Journal of Agricultural Sciences, 47(4), 171-174.
Kumari, P., Prasad, R., Kumari, S. Yadav, M., D., Prasad, R., & Prasad, D. (2019). Bioefficacy of some botanical and chemical insecticides against yellow stem borer Scirpophaga incertulas (Walk.) In rice field at Jharkhand. Journal of Pharmacognosy and Phytochemistry, 2, 200–203.
Madhu, B., Warghat, A. N., & Tayde, A. R. (2020). Comparative effect of bio pesticides and neem commercial products on rice yellow stem borer, Scirpophaga incertulas (Walker). Journal of Entomology and Zoology Studies, 8(1), 758–760. http://www.entomoljournal.com
MoALD, (2020). Statistical Information on Nepalese Agriculture 2018/2019.Agri Statistics Section, Monitoring, Evaluation and Statistics Division. Singha Durbar, Kathmandu, Nepal: Ministry of Agricultural Development.
Ogah, O., Omoloye, A., Nwilene, F., & Nwogbaga, A. (2011). Effect of neem seed kernel extracts in the management of rice stem borers in the field in Nigeria. Nigerian Journal of Biotechnology, 23, 13–21.
Pokhrel, A., Dhakal, S., Kafle, R., & Pokhrel, A. (2021). Adoption status of improved production technology in rice cultivation in Kanchanpur, Nepal. Archives of Agriculture and Environmental Science, 6(2), 178–185, https://doi.org/10.26832/24566632.2021.060209
Prasad, S. S., Gupta, P. K., & Kanaujia, B. L. (2004). Simulation study on yield loss due to Scirpophaga incertulas on semi deep water rice. Annuals of Plant Protection Sciences, 15, 491492
Rajput, V. S., Jhala, J., & Acharya, V. (2020). Biopesticides and their mode of action against insect pests: A review. International Journal of Chemical Studies, 8(2), 2856–2862, https:/doi.org/10.22271 chemi.2020.v8.i2ar.9184
Singh, B., & Chatterjee, S. (2021). Relative efficacy of some biorational and microbial insecticides against yellow stem borer and whorl maggot of boro paddy. Journal of Biopesticides, 14(2),90–96.
Singh, P., Dhaka, R. S., Kumar, S. S., Kumar, D., & Kumari, H. (2015). Bioefficacy of insecticides and bio-pesticides against yellow stem borer, Scirpophaga incertulus (Walk.) and their effect on spiders in rice crop. South Asian Journal of Food Technology and Environment, 1(2), 179-183.
Singh, P., & Choudhary, P. K. (2018). Efficacy of Bacillus thuringiensis against yellow stem borer in rice: A review. International Journal of Current Microbiology and Applied Sciences, 7(4), 2249-2258.
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2023 Agriculture and Environmental Science Academy

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.




