Seed germination and seedling development of spring wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) landraces under elevated salinity conditions
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.26832/24566632.2024.0903017Keywords:
Mudule, Salinity stress, Seedling stage, Wheat landracesAbstract
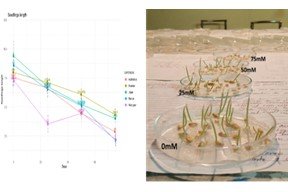
Due to osmotic stress, ion toxicity, and nutrient imbalances, salinity is a common environmental problem that affects about 20.87% of agricultural land. It severely limits crop production, including wheat, by making it harder for seeds to germinate and for seedlings to grow. To study the effect of salinity stress on wheat landraces, we aimed to examine the seedling characteristics of wheat landraces under salinity stress. The study followed a two-factor Completely Randomized Design (CRD) with four replications. Four different concentrations of NaCl (0 mM, 25 mM, 50 mM, 75 mM) and five landraces (Bhartale, Jhuse, Rato Gahun, Mudule, and Aadhikhole) were used for investigation during the germination and early seedling stages of wheat landraces. The highest germination percentage (GP) (97.25%) and seed vigour index (SVI) (92886) were observed in Jhuse, whereas the lowest GP (60.50%) and SVI (11494) were observed in Rato Gahun. Rato gahun had the highest mean germination time (5.99 days), and Mudule had the lowest mean germination time (4.82 days). The maximum fresh weight (0.12 g) and dry weight (DW) (0.042 g) were recorded by Aadhikhole and Jhuse, and the minimum fresh weight (DW) (0.10 g) and DW (0.032 g) were observed in Mudule. The maximum shoot and root lengths were observed in Bhartale (3.05 cm) and Jhuse (3.54 cm), whereas the minimum shoot length (SL) (2.07 cm) and root length (RL) (2.41 cm) were observed in Rato Gahun. Above all, salinity stress negatively impacts wheat seedling characteristics, and Mudule shows some promising stress tolerance compared to others.
Downloads
References
Abbasdokht, H., Edalatpishe, M. R., & Gholami, A. (2010). The effect of hydropriming and halopriming on germination and early growth stage of wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). Journal of Stress Physiology & Biochemistry, 4(8), 984–988.
Abdoli, M., Saeidi, M., Azhand, M., Jalali-Honarmand, S., Esfandiari, E., & Shekari, F. (2013). The effects of different levels of salinity and indole-3-acetic acid (IAA) on early growth and germination of wheat seedling. Journal of Stress Physiology & Biochemistry, 9(4), 329–338.
Adhikari, B., Dhital, P. R., Ranabhat, S., & Poudel, H. (2021). Effect of seed hydro-priming durations on germination and seedling growth of bitter gourd (Momordica charantia). PLoS ONE, 16(8), Article e0255258. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0255258
Adilu, G. S., & Gebre, Y. G. (2021). Effect of salinity on seed germination of some tomato (Lycopersicon esculentum Mill.) varieties. Journal of Aridland Agriculture, 7, 76–82. https://doi.org/10.25081/jaa.2021.v7.6588
Akbarimoghaddam, H., Galavi, M., Ghanbari, A., & Panjehkeh, N. (2011). Salinity effects on seed germination and seedling growth of bread wheat cultivars. Trakia journal of Sciences, 9(1), 43-50.
Alharbi, K., Al-Osaimi, A. A., & Alghamdi, B. A. (2022). Sodium chloride (NaCl)-induced physiological alteration and oxidative stress generation in Pisum sativum (L.): A toxicity assessment. ACS Omega, 7(24), 20819–20832. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsomega.2c01427
Biswas, S., Seal, P., Majumder, B., & Biswas, A. K. (2023). Efficacy of seed priming strategies for enhancing salinity tolerance in plants: An overview of the progress and achievements. Plant Stress, 9, Article 100186. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.stress.2023.100186
Chen, J., Liu, Y., Zhang, T., Zhou, Z., Huang, J., Zhou, T., & Hua, Y. (2022). Integrated physiological and transcriptional dissection reveals the core genes involving nutrient transport and osmoregulatory substance biosynthesis in allohexaploid wheat seedlings under salt stress. BMC Plant Biology, 22(1), Article 502. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12870-022-03887-0
Cheng, H., Ye, M., Wu, T., & Ma, H. (2023). Evaluation and heritability analysis of the seed vigor of soybean strains tested in the Huanghuaihai regional test of China. Plants, 12(6), Article 1347. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants12061347
de la Reguera, E., Veatch, J., Gedan, K., & Tully, K. L. (2020). The effects of saltwater intrusion on germination success of standard and alternative crops. Environmental and Experimental Botany, 180, Article 104254. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envexpbot.2020.104254
Demir, I., Ermis, S., Mavi, K., & Matthews, S. (2008). Mean germination time of pepper seed lots (Capsicum annuum L.) predicts size and uniformity of seedlings in germination tests and transplant modules. Seed Science and Technology, 36(1), 21–30. https://doi.org/10.15258/sst.2008.36.1.02
Devi, S., Phogat, D. S., Singh, S., & Jangra, M. (2021). Physiological performance of oat under salt stress. Journal of Agricultural Science, 13, 18–21.
Ehtaiwesh, A. F., & Rashed, F. H. (2019). The effect of salinity on Libyan soft wheat Triticum aestivum L. at germination stage. Scientific Journal of Applied Sciences of Sabratha University, 2(2), 41–54. https://doi.org/10.47891/sabujas.v2i2.41-54
Gola, A. Q. (2018). Effect of salt (NaCl) stress on germination and early seedling growth of muskmelon (Cucumis melo L.). Pure and Applied Biology, 7(4), Article 218. https://doi.org/10.19045/bspab.2018.700218
Hasanuzzaman, M., Hakeem, K. R., Nahar, K., & Alharby, H. F. (2019). Plant abiotic stress tolerance: Agronomic, molecular and biotechnological approaches. Springer. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-06118-0
Hopmans, J. W., Qureshi, A. S., Kisekka, I., Munns, R., Grattan, S. R., Rengasamy, P., Ben-Gal, A., Assouline, S., Javaux, M., Minhas, P. S., Raats, P. A. C., Skaggs, T. H., Wang, G., De Jong van Lier, Q., Jiao, H., Lavado, R. S., Lazarovitch, N., Li, B., & Taleisnik, E. (2021). Critical knowledge gaps and research priorities in global soil salinity. Advances in Agronomy, 169, 1–191. https://doi.org/10.1016/bs.agron.2021.03.001
Irik, H. A., & Bikmaz, G. (2024). Effect of different salinity on seed germination, growth parameters and biochemical contents of pumpkin (Cucurbita pepo L.) seeds cultivars. Scientific Reports, 14(1), Article 6929. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-024-55325-w
Jaradat, A. A. (2013). Wheat landraces: A mini review. Emirates Journal of Food and Agriculture, 25(1), 20–29. https://doi.org/10.9755/ejfa.v25i1.15376
Khare, T., Kumar, V., & Kishor, P. B. K. (2015). Na+ and Cl− ions show additive effects under NaCl stress on induction of oxidative stress and the responsive antioxidative defense in rice. Protoplasma, 252(4), 1149–1165. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00709-014-0749-2
Liu, Y., Su, M., & Han, Z. (2022). Effects of NaCl stress on the growth, physiological characteristics and anatomical structures of Populus talassica × Populus euphratica seedlings. Plants, 11(22), Article 3025. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants11223025
Mbarki, S., Skalicky, M., Vachova, P., Hajihashemi, S., Jouini, L., Zivcak, M., Tlustos, P., Brestic, M., Hejnak, V., & Zoghlami Khelil, A. (2020). Comparing salt tolerance at seedling and germination stages in local populations of Medicago ciliaris L. to Medicago intertexta L. and Medicago scutellata L. Plants, 9(4), Article 526. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants9040526
MoALD. (2023). Statistical information on Nepalese agriculture 2078/79 (2021/22). Ministry of Agriculture and Livestock Development. https://doi.org/10.1515/aucft-2017-0005
Muhammad, Z., & Hussain, F. (2012). Effect of NaCl salinity on the germination and seedling growth of seven wheat genotypes. Pakistan Journal of Botany, 44(6), 1845–1850.
Munns, R., & Tester, M. (2008). Mechanisms of salinity tolerance. Annual Review of Plant Biology, 59(1), 651–681. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.arplant.59.032607.092911
Munns, R., James, R. A., & Läuchli, A. (2006). Approaches to increasing the salt tolerance of wheat and other cereals. Journal of Experimental Botany, 57(5), 1025–1043. https://doi.org/10.1093/jxb/erj100
Nasri, N., Kaddour, R., Rabhi, M., Plassard, C., & Lachaal, M. (2011). Effect of salinity on germination, phytase activity and phytate content in lettuce seedling. Acta Physiologiae Plantarum, 33(3), 935–942. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11738-010-0625-4
Noreen, Z., Ashraf, M., & Mahmood-ul-Hassan. (2007). Inter-accessional variation for salt tolerance in pea (Pisum sativum L.) at germination and screening stage. Pakistan Journal of Botany, 39(6), 2075–2085.
Pervaiz, S., Saqib, M., Akhtar, J., Riaz, M. A., Anwar-ul-Haq, M., & Nasim, M. (2007). Comparative growth and leaf ionic composition of four cotton (Gossypium hirsutum L.) genotypes in response to salinity. Pakistan Journal of Agricultural Sciences, 44(1), 79–84.
R, N., VH, A., Patil, M., UV, M., & BO, K. (2024). Effect of salinity stress on morphophysiological traits in chickpea genotypes. International Journal of Research in Agronomy, 7(1), 258–262. https://doi.org/10.33545/2618060x.2024.v7.i1d.225
Rakic, T., Pesic, M., Kostic, N., et al. (2021). Rhizobacteria associated with Miscanthus x giganteus improve metal accumulation and plant growth in the flotation tailings. Plant and Soil, 462(1), 349–363.
Rutala, W. A., & Weber, D. J. (2014). Disinfection, sterilization, and control of hospital waste. In Mandell, Douglas, and Bennett’s principles and practice of infectious diseases (8th ed., Vol. 2, pp. 3294–3309.e1). Elsevier Inc.
https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-1-4557-4801-3.00301-5
Sarlach, R. S., Sharma, A., & Bains, N. S. (2013). Seed priming in wheat: Effect on seed germination, yield parameters, and grain yield. Progressive Research, 8(1), 109–112.
Singh, R., & Rakesh Singh, C. (2017). Effects of hydro priming on seed germination and vigour of Aegle marmelos. Journal of Pharmacognosy and Phytochemistry, 6(5), 446–449.
Song, P., Zhao, B., Sun, X., Li, L., Wang, Z., Ma, C., & Zhang, J. (2023). Effects of Bacillus subtilis HS5B5 on maize seed germination and seedling growth under NaCl stress conditions. Agronomy, 13(7), Article 1874. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy13071874
Tabatabaei, S. A. (2014). The effect of halo- and hydro-priming on seed reserve utilization and seed germination of wheat seeds under salinity stress. Cercetari Agronomice in Moldova, 47(3), 39–45. https://doi.org/10.2478/cerce-2014-0025
Uçarlı, C. (2021). Effects of salinity on seed germination and early seedling stage. In Abiotic stress in plants. IntechOpen. https://doi.org/10.5772/intechopen.93647
Wahid, A., Perveen, M., Gelani, S., & Basra, S. M. A. (2007). Pretreatment of seed with H2O2 improves salt tolerance of wheat seedlings by alleviation of oxidative damage and expression of stress proteins. Journal of Plant Physiology, 164(3), 283–294. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jplph.2006.01.005
Yusufe, M., Mohammed, A., & Satheesh, N. (2017). Effect of duration and drying temperature on characteristics of dried tomato (Lycopersicon esculentum L.) Cochoro variety. Acta Universitatis Cibiniensis - Series E: Food Technology, 21(1), 41–50. https://doi.org/10.1515/aucft-2017-0005
Zhang, Y., Kaiser, E., Marcelis, L. F. M., Yang, Q., & Li, T. (2020). Salt stress and fluctuating light have separate effects on photosynthetic acclimation, but interactively affect biomass. Plant, Cell & Environment, 43(9), 2192–2206. https://doi.org/10.1111/pce.13810
Zou, Y., Zhang, Y., & Testerink, C. (2022). Root dynamic growth strategies in response to salinity. Plant, Cell & Environment, 45(3), 695–704. https://doi.org/10.1111/pce.14205
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2024 Agriculture and Environmental Science Academy

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.




