Effect of nitrogen levels on growth and yield of popcorn maize (Zea mays var. everta) in Mid Hills, Parbat District, Nepal
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.26832/24566632.2024.090308Keywords:
Growth, Nitrogen dose, Popcorn, Toxicity, YieldAbstract
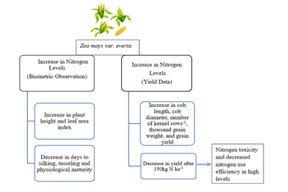
A field experiment was conducted from March to July 2020 to investigate the impact of varying nitrogen levels on the growth and yield of popcorn maize in Parbat. The experiment was laid out in single factorial Randomized Complete Block Design (RCBD) comprising nine levels of nitrogen: 0, 50, 75, 100, 120, 125, 150, 175 and 200 kg ha-1 as treatment with three replications. "Lumle Yellow" variety was cultivated in an acidic (pH 4.9) clay loam soil with moderate levels of total nitrogen (0.19%), high levels of available phosphorus (126.6 kg ha-1), potassium (427.68 kg ha-1), and moderate organic matter content (4.36%). The findings showed that an increased N-level significantly increased plant height and the leaf area index, reaching a maximum at 175 kg N ha-1. While number of cob plant-1 and kernel row cob-1 were non-significant, yield attributing parameters such as cob length, cob diameter, number of kernel rows-1, thousand grain weight, and grain yield were significant and determined to be maximum at 150 kg N ha-1. With subsequent increases in N to 175 and 200 kg N ha-1, the yield-attributing features did not show an increase. The highest grain yield (4.97 Mt ha-1) produced from 150 kg N ha-1 was 98 percent higher than the yield obtained from control (2.5 Mt ha-1) and 28 percent higher as compared to lowest level of N (50 kg ha-1). However, reduction in grain yield was found with increase in N levels above 150 kg ha-1.
Downloads
References
Adhikari, K., Bhandari, S., Aryal, K., Mahato, M., & Shrestha, J. (2021). Effect of different levels of nitrogen on growth and yield of hybrid maize (Zea mays L.) varieties. Journal of Agriculture and Natural Resources, 4(2), 48–62. https://doi.org/10.3126/janr.v4i2.33656
Ahmad, S., Khan, A. A., Kamran, M., Ahmad, I., Ali, S., & Fahad, S. (2018). Response of Maize Cultivars to Various Nitrogen Levels. European Journal of Experimental Biology, 08(01). https://doi.org/10.21767/2248-9215.100043
AKC. (2019). Annual report by Agriculture Knowledge Centre, Parbat.
Amanullah. (2014). Source and rate of nitrogen application influence agronomic N-use efficiency and harvest index in maize (Zea mays L) genotypes. Maydica Electronic Publication, 80–89.
Binder, D. L., Sander, D. H., & Walters, D. T. (2000). Maize response to time of nitrogen application as affected by level of nitrogen deficiency. Agronomy Journal, 92(6), 1228–1236. https://doi.org/10.2134/AGRONJ2000.9261228X
Dawadi, D., & Sah, S. (2012). Growth and Yield of Hybrid Maize (Zea mays L.) in Relation to Planting Density and Nitrogen Levels during Winter Season in Nepal. Tropical Agricultural Research, 23(3), 218. https://doi.org/10.4038/tar.v23i3.4659
Derby, N. E., Casey, F. X. M., Knighton, R. E., & Steele, D. D. (2004). Midseason Nitrogen Fertility Management for Corn Based on Weather and Yield Prediction. Agronomy Journal, 96(2), 494–501. https://doi.org/10.2134/AGRONJ2004.4940
Gaire, R., Pant, C., Sapkota, N., Dhamaniya, R., & Bhusal, T. N. (2020). Effect of Spacing and Nitrogen Level on Growth and Yield of Maize (Zea mays L.) in Mid hill of Nepal. Malaysian Journal of Halal Research, 3(2), 50–55. https://doi.org/10.2478/MJHR-2020-0009
Gheith, E. M. S., El-Badry, O. Z., Lamlom, S. F., Ali, H. M., Siddiqui, M. H., Ghareeb, R. Y., El-Sheikh, M. H., Jebril, J., Abdelsalam, N. R., & Kandil, E. E. (2022). Maize (Zea mays L.) Productivity and Nitrogen Use Efficiency in Response to Nitrogen Application Levels and Time. Frontiers in Plant Science, 13. https://doi.org/10.3389/FPLS.2022.941343
Gökmen, S., Sencar, O., & Sakin, M. A. (2001). Response of popcorn (Zea mays everta) to nitrogen rates and plant densities. Turkish Journal of Agriculture and Forestry, 25(1), 15–23. https://doi.org/10.3906/tar-9904-20
Gözübenli, H., & Konukan, Ö. (2010). Nitrogen dose and plant density effects on popcorn grain yield. African Journal of Biotechnology, 9(25), 3828–3832. http://www.academicjournals.org/AJB
Gul, S., Khanday, B. A., & Khan, M. H. (2016). Effect of fertility levels and herbicide mixtures on yield and yield attributes of rainfed maize under temperate conditions of Kashmir. Applied Biological Research, 18(2), 185. https://doi.org/10.5958/0974-4517.2016.00028.8
Gungula, D., Togun, A., & Kling, J. (2007). The Effects of Nitrogen Rates on Phenology and Yield Components of Early Maturing Maize Cultivars. Global Journal of Pure and Applied Sciences, 13(3), 319–324.
Hammad, H. M., Ahmad, A., Farhad, W., Abbas, F., Qasim, K., & Saeed, S. (2013). Nitrogen stimulates phenological traits, growth and growing degree days of maize. Pakistan Journal of Agricultural Sciences, 50(3), 337–343.
Hammad, H. M., Chawla, M. S., Jawad, R., Alhuqail, A., Bakhat, H. F., Farhad, W., Khan, F., Mubeen, M., Shah, A. N., Liu, K., Harrison, M. T., Saud, S., & Fahad, S. (2022). Evaluating the Impact of Nitrogen Application on Growth and Productivity of Maize Under Control Conditions. Frontiers in Plant Science, 13, 885479. https://doi.org/10.3389/FPLS.2022.885479/BIBTEX
Huffman, J. . (1989). Effects of enhanced ammonium nitrogen availability for corn. J. Agron.Educ., 18(2). https://doi.org/10.2134/agronmonogr10.c13
Iqbal, M. A., Ahmad, Z., Maqsood, Q., Afzal, S., & Ahmad, M. M. (2015). Optimizing Nitrogen Level to Improve Growth and Grain Yield of Spring Planted Irrigated Maize (Zea mays L.). Journal of Advanced Botany and Zoology, January, 1–4. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/278019892
Jasemi, M., Darabi, F., Naseri, R., Naserirad, H., & Bazda, S. (2013). Effect of Planting Date and Nitrogen Fertilizer Application on Grain Yield and Yield Components in Maize (SC 704). American-Eurasian Journal of Agricultural & Environmental Sciences , 13(7), 914–919.
Jugenheimer, R. W. (1976). Corn: improvement, seed production, and uses. John Wiley and Sons, 670.
Karki, M., Panth, B. P., Subedi, P., GC, A., & Regmi, R. (2020). Effect of Different Doses of Nitrogen on Production of Spring Maize (Zea Mays) in Gulmi, Nepal. Sustainability in Food and Agriculture, 1(1), 01–05. https://doi.org/10.26480/sfna.01.2020.01.05
MoALD. (2022). Ministry of Agriculture and Livestock Development. Satistical Information on Nepalese Agriculture. https://www.moald.gov.np/publication/Agriculture Statistics
Arif, M. S. I. (2015). Effect of Nitrogen Levels and Plant Population on Yield and Yield Components of Maize. Advances in Crop Science and Technology, 03(02). https://doi.org/10.4172/2329-8863.1000170
Omar, S., Abd Ghani, R., Khaeim, H., Sghaier, A. H., & Jolánkai, M. (2022). The effect of nitrogen fertilisation on yield and quality of maize (Zea mays L.). Acta Alimentaria, 51(2), 249–258. https://doi.org/10.1556/066.2022.00022
Rai, K. (1961). The response of maize following sorghum to fertilisers and foliar spray of zinc sulphate at Tozi, Sudan. https://www.cabidigitallibrary.org/doi/full/10.5555/19631700120
Russell, W. A., & Hallauer, A. R. (1980). Corn. Hybridization of Crop Plants, 299–312. https://doi.org/10.2135/1980.HYBRIDIZATIONOFCROPS.C19
Saleem, M., Javed, S., Mukhtar, R., Khan, K. M., Shoaib, M., Ikram, M., & Hassan, A. (2017). Impact of different doses of nitrogen on growth and yield of maize in agro-ecological zone of district Vehari. International Journal of Current Research in Biology and Medicine, 2(7), 34–37. https://doi.org/10.22192/ijcrbm
Santos, P. G., Cezar, J. F., Buiatti, A. L., & Toshiyuki, H. O. (2002). Evaluation of the agronomic performance of corn hybrids in Uberlândia, MG, Brazil. Pesquisa Agropecuária Brasileira, 37(5), 597–602.
Schepers, A. (1990). Popcorn takes on new flavors, fat and sodium. Environmental Nutrition (USA), 4–5.
Shrestha, J., Nath Yadav, D., Prasad Amgain, L., & Prasad Sharma, J. (2018). Effects of Nitrogen and Plant Density on Maize (Zea mays L.) Phenology and Grain Yield. Current Agriculture Research Journal, 6(2), 175–182. https://doi.org/10.12944/CARJ.6.2.06
Stark, C. H., & Richards, K. (2008). The continuing challenge of nitrogen loss to the environment: Environmental consequences and mitigation strategies. Dynamic Soil, Dynamic Plant, 2(2), 41–55.
Tamang, S., Tamang, A., & Magar, S. R. (2024). Effect of Different Doses of Nitrogen on Growth and Grain Yield of Hybrid Maize (Zea mays L., Gold 97). AgroEnvironmental Sustainability, 2(2), 84–93. https://doi.org/10.59983/s2024020203
Turgut, I. (2000). Effects of Plant Populations and Nitrogen Doses on Fresh Ear Yield and Yield Components of Sweet Corn (Zea mays saccharata Sturt.). Turkish Journal of Agriculture and Forestry, 24(3).
Türk, M., & Alagöz, M. (2018). The Effect of Nitrogen Fertilizer on the Yield and Quality in the Sweet Maize. ISSN 2285-5785
USDA. (2020). USDA ERS - Nutrient Management. Economic Research Service U.S. Department of Agriculture. https://www.ers.usda.gov/topics/farm-practices-management/crop-livestock-practices/nutrient-management/
Zhang, X., Meng, F., Li, H., Wang, L., Wu, S., Xiao, G., & Wu, W. (2019). Optimized fertigation maintains high yield and mitigates N2O and NO emissions in an intensified wheat–maize cropping system. Agricultural Water Management, 211, 26–36. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agwat.2018.09.045
Ziegler, K. . (2001). Popcorn.In A. R. Hallauer (Ed.). Specialty Corns (2nd Ed., 199–234.
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2024 Agriculture and Environmental Science Academy

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.




