Integrative approaches to understanding mercury toxicity in common bean (Phaseolus vulgaris) plants: Linking growth, biochemistry and antioxidant mechanisms
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.26832/24566632.2024.0904020Keywords:
Common Beans, Heavy metals, Mercury, Pollution, ToxicityAbstract
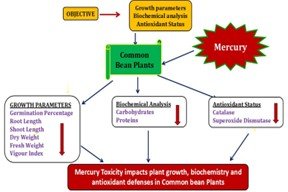
Mercury is a widely studied toxic metal all over the world due to its ability to easily enter into the food chain. Even exposure to small quantities, causes adverse effects on various biochemical and physiological processes. This study aimed to investigate the integrative approaches to understanding mercury toxicity in common bean (Phaseolus vulgaris) plants by linking growth, biochemistry and antioxidant mechanisms. Experimental common bean plants were divided into 4 groups. Group 1 served as control, received normal nutritional and water support, while Group 2, 3 and 4 were treated with mercury concentrations of 50, 100 and 200 mg respectively. The results revealed that mercury treated common bean plants exhibited a significant decline in several key growth and physiological parameters, including germination percentage, root length, shoot length, fresh weight, dry weight and vigor index. Moreover, mercury treatment leads to reduction in carbohydrate and protein contents, as well as reduced activities of antioxidant enzymes like catalase and superoxide dismutase. These findings underscore the significance of further research to identify strategies for alleviating mercury-induced toxicity and enhancing plant resilience, with the goal of contributing to the development of sustainable agricultural practices that enhance the crop resilience in polluted environments.
Downloads
References
Abdul-Baki, A. A., & Anderson, J. D. (1973). Vigor determination in soybean seed by multiple criteria. Crop Science, 13, 630-633.
Asano S., Eto, K., Kurisaki, E., Gunji. H., Hiraiwa, K., Sato, M., Sato, H., Hasuike, M., Hagiwara, N., & Wakasa, H. (2000). Acute inorganic mercury vapour inhalation poisoning. Pathology International, 50, 169-174.
Assche, F., & Clijsters, H. (1990). Effects of metals on enzyme activity in plants. Plant, Cell and Environment, 24, 1-15.
Atchibri, O. A. A. L., Brou. K. D., Kouakou, T. H., Kouadio, Y. J., & Gnakri, D. (2010). Screening for anti-diabetic activity and phytochemical constituents of common bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.) seeds. Journal of Medicinal Plants Research, 4(17), 1757-1761.
Ben, Y., Cheng, M., Liu, Y., Wang, L., Yang, Q., Huang, X., & Zhou, Q. (2023). The stimulatory effect and mechanism of low-dose lanthanum on soybean leaf cells. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 441, 129924.
Bennett, L. E., Burkhead, J. L., Hale, K.L., Terry, N., Pilon, M., & Pilon-smits, E. A. H. (2003). Analysis of transgenic Indian Mustard plants for phytoremediation of metals-contaminated mine tailings. Journal of Environmental Quality, 32, 432-440.
Blaylock, M. J., & Huang, J. W. (2000). “Phytoextraction of metals,” in Phytoremediation of Toxic Metals: Using Plants to Clean up the Environment, I. Raskin and B. D. Ensley, Eds., Wiley, New York, NY, USA, 53-70.
Briffa, J., Sinagra, E., & Blundell, R. (2020). Heavy Metal Pollution in the Environment and Their Toxicological Effects on Humans. Heliyon, 6 (9), e04691.
Caroli, M.D., Furini, A., DalCorso, G., Rojas, M., & Sansebastiano, G.P.D. (2020). Endomembrane Reorganization Induced by Heavy Metals. Plants, 9, 482.
Chakraborty, D., & Choudhury, B. (2023). Toxic effects of Mercury on crop plants and its Physiological and Biochemical responses - A Review. International Journal of Advanced Research, 11(2), 168-174.
Chen, C. W., Chen. C. F., & Dong, C. D. (2012). Distribution and Accumulation of Mercury in Sediments of Kaohsiung River Mouth, Taiwan. APCBEE Procedia, 1, 153–158.
Cyboran-Mikolajczyk, S., Meczarska, K., Solarska-Sciuk, K., Ratajczak-Wielgomas, K., Oszmianski, J., Jencova, V., & Bonarska-Kujawa, D. (2022). Protection of Erythrocytes and Microvascular Endoth elial Cells against Oxidative Damage by Fragaria vesca L. and Rubus idaeus L. Leaves Extracts-The Mechanism of Action. Molecules, 27, 5865.
D’Souza, C., & Peretiatko, R., (2002). The nexus between industrialization and environment: A case study of Indian enterprises. Environmental Management and Health, 13, 80–97.
Djingova, R., & Kuleff, I. (2000). Instrumental Techniques for Trace Analysis. In: Vernet, J.P., Ed., Trace Elements: Their Distribution and Effects in the Environment. Elsevier Science Ltd., United Kingdom. 137-185.
Duan, Y., Sangani, C. B., Muddassir, M., Soni, K. V. (2020). Copper, Chromium and Nickel Heavy metal effects on total sugar and protein content in Glycine Max. Research square.
Finley, J. W., Burrell, J. B., & Reeves, P.G. (2007). Pinto bean consumption changes SCFA profiles in fecal fermentations, bacterial populations of the lower bowel, and lipid profiles in blood of humans. The Journal of Nutrition, 137, 2391-2398.
Fujii, J., Homma, T., Osaki, T. (2022). Superoxide Radicals in the Execution of Cell Death. Antioxidants, 11, 501.
Georgiadou, E. C., Kowalska, E., Patla, K., Kulbat, K., Smolin, ska, B., Leszczyn, ska, J., & Fotopoulos, V. (2018). Influence of Heavy Metals (Ni, Cu, and Zn) on Nitro-Oxidative Stress Responses, Proteome Regulation and Allergen Production in Basil (Ocimum basilicum L.) Plants. Frontiers in Plant Science, 9, 862.
Gupta, A. K., Negi, M., Nandy, S., Alatalo, J. M., Singh, V., & Pandey R (2019). Assessing the vulnerability of socio-environmental systems to climate change along an altitude gradient in the Indian Himalayas. Ecological Indicators, 106, 105512.
Gupta, A., Agarwal, N. K., & Byadgi, P. S. (2014). Clinical assessment of dietary interventions and lifestyle modifications in Madhumeha (type-2 diabetes mellitus). Ayurveda, 35, 391–397.
Hangen, L., & Bennink, M. R. (2002). Consumption of black beans and navy beans (Phaseolus vulgaris) reduced azoxymethane-induced colon cancer in rats. Nutrition and Cancer, 44(1), 60-5.
Hedge, J. E., & Hofreiter, B. T. (1962). In Carbohydrate chemistry 17 (Eds Whistler RL and Be Miller JN). Academic press. New York.
Hu, Y., Li, J., Lou, B., Wu, R., Wang, G., Lu, C., Wang, H., Pi, J., & Xu, Y. (2020). The Role of Reactive Oxygen Species in Arsenic Toxicity. Biomolecules, 10(2), 240.
Kakkar, P. S., Das, B., & Viswanathan, P. N. (1984). A modified spectrophotometeric assay for superoxide dismutase. Indian Journal of Biochemistry and Biophysics, 21, 130-132.
Khalid M. F., Morillon R., Anjum M. A., Ejaz S., Rao M. J., Ahmad, S., & Hussain, S. (2022). Volkamer lemon tetraploid rootstock transmits the salt tolerance when grafted with diploid kinnow mandarin by strong antioxidant defense mechanism and efficient osmotic adjustment. Journal of Plant Growth Regulation, 41(3), 1125-1137.
Kumar, V., & Chopra, A. K. (2013). Accumulation and translocation of metals in soil and different parts of French bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.) amended with sewage sludge. Bulletin of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 92(1), 103-108.
Kumar, V., & Chopra, A. K. (2014a). Ferti-irrigational impact of sugar mill effluent on agronomical characteristics of Phaseolus vulgaris (L.) in two seasons. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 186, 7877–7892.
Kumar, V., & Chopra, A. K. (2014b). Ferti-irrigation effect of paper mill effluent on agronomical practices of Phaseolus vulgaris (L.) in two different seasons. Communications in Soil Science and Plant Analysis, 45, 2151–217.
Kumar, V., Kumar, P., & Khan, A. (2020). Optimization of PGPR and silicon fertilization using response surface methodology for enhanced growth, yield and biochemical parameters of French bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.) under saline stress. Biocatalysis and Agricultural Biotechnology, 23, 101463.
Kumari, S., Kumar, V., Kothari, R., & Kumar, P. (2022). Effect of supplementing biochar obtained from different wastes on biochemical and yield response of French bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.): An experimental study. Biocatalysis and Agricultural Biotechnology, 43, 102432.
Lowry, O. H., Roseborough, N. J., Farr, A. L., & Randall, R. L. (1951). Protein measurement with Folin-phenol reagent. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 193, 265-275.
Maruyama, C., Araki, R., Kawamura, M., Kondo, N., Kigawa, M., & Kawai, Y. (2008). Azuki bean juice lowers serum triglyceride concentrations in healthy young women. Journal of Clinical Biochemistry and Nutrition, 43, 19-25.
Meharg, A. A. (2004). Arsenic in rice–understanding a new disaster for south-east Asia. Trends in Plant Science, 9, 415-417.
Mohapatra, M., Sethy, P. R., Routray, P., Mallick, R., & Padhi, S. (2021). Ecophysiological Studies of Vigna mungo L. Seedlings with Mercuric Chloride (HgCl2) Stress. Scholars Academic Journal of Biosciences, 9(3), 58-62.
Namburu, S. L., Dodoala, S., Bharathi, K., Prasad, K. V. S. R. G. (2017). Anti-urolithiatic activity of Phaseolus vulgaris seeds against ethylene glycol-induced renal calculi. in Wistar rats. International Journal of Green Pharmacy, 11(4), 284.
Porch, T. G, Beaver, J. S., Debouck, D. G., Jackson, S. A., & Kelly, J. D. (2013). Use of wild relatives and closely related species to adapt common bean to climate change. Agronomy, 3(2), 433-461.
Reverri, E. J., Randolph, J. M., Steinberg, F. M., Kappagoda, C. T., Edirisinghe, I., Burton-Freeman, B. M. (2015). Black beans, fiber, and antioxidant capacity pilot study: Examination of whole foods vs. functional components on postprandial metabolic, oxidative stress, and inflammation in adults with metabolic syndrome. Nutrients, 7, 6139-6154.
Shourie, A. (2022). Effect of Cadmium and Lead Stress on Seed Germination and Seedling Growth of Jatropha curcas L. Bioscienes Biotechnology Research Asia, 19(3), 671-678.
Singh, V., & Mishra, V. (2021). Microbial Removal of Cr (VI) by anew Bacterial Strain Isolated from the Site Contaminated with Coal Mine Effluents. Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering, 9(5), 106279.
Singh, V., Singh, N., Verma, M., Kamal, R., Tiwari, R., Chivate, M. S., Rai, S. N., Kumar, A., Singh, A., Singh, M. P, Vamanu, E., & Mishra, V. (2022). Hexavalent-Chromium-Induced Oxidative Stress and the Protective Role of Antioxidants Against Cellular Toxicity. Antioxidants, 1(12), 2375.
Sinha, K. A. (1972). Colorimetric assay of catalase. Analytical Biochemistry, 47, 389-394.
Talha, J., Mehnaz, K., & Sanjay, K. (2017). Antihypertensive effect of the alcoholic extract of seeds of Phaseolus vulgaris Linn. (Fabaceae) on high salt diet induced Hypertension in Male rats, International Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences and Research, 8(7), 3092-3097.
USEPA (2001) EPA/Water Quality, Environmental Matters. Environmental Protection Agency, United States, 76.
Vijay, M., Binu, G., & Eswari, K. (2024). Bioaccumulation of Mercury and its consequences on morphological and biochemical parameters in Fenugreek (Trigonella foenum-graecum L.). Journal of Chemical Health Risks, 14(6), 157-169.
Vijay, M., Binu, G., Keerthana, S. (2024). Toxicological impacts of mercury on the growth and biochemical profiles of pumpkin (Curcurbita moschata duchesne). World Journal of advanced Research and Reviews, 24(1), 2596-2605.
Yang, Q. Q., Gan, R. Y, Ge, Y. Y., Zhang, D., & Corke, H. (2018). Polyphenols in Common Beans (Phaseolus vulgaris L.): Chemistry, Analysis and Factors Affecting Composition. Comprehensive Reviews in Food Science and Food Safety,17(6), 1518-1539.
Zaynab, M., Al-Yahyai, R., Ameen, A., Sharif, Y., Ali, L., Fatima, M., Khan, K. A., & Li, S. (2022). Health and Environmental Effects of Heavy Metals. Journal of King Saud University, 34(1), 101653.
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2024 Agriculture and Environmental Science Academy

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.




