Probiotics in aquaculture: A pathway to safer and healthier fish farming
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.26832/24566632.2024.0904030Keywords:
Aquaculture, Probiotic bacteria, Fish, Disease resistance, Immune systemAbstract
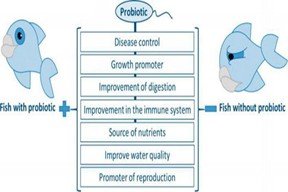
Aquaculture benefits greatly from probiotic bacteria, which are also very helpful in preventing a number of infectious diseases. They can be use in place of antibiotics and antimicrobials. Fish that take probiotics have stronger immune systems and grow faster. They aid in the elimination of heavy metals in addition to fostering fish development. Although probiotics can be extracted from a variety of sources, the fish's own stomach is the best source for probiotics. The source of putative probiotics is the same as that of the organism ingesting them. Potential probiotics can flourish in the fish gastrointestinal tract since they are already acclimated to the conditions of the fish gut. Numerous bacteria have been used as probiotics in various experiments, primarily as a feed supplement at varying concentrations. Fish treated with probiotic bacteria have shown positive effects such as improved growth with lower production costs, improved reproductive performances, improved immunology, and disease resistance. When utilized in place of commercial antibiotics and antimicrobials, which can lead to resistance against bacterial species when overused, probiotics can be advantageous for fish farmers. In this paper, aquaculture probiotics, their types, work of mechanism and their uses have been discussed for sustainable aquaculture productivity.
Downloads
References
Akhter, N., Wu, B., Memon, A. M., & Mohsin, M. (2015). Probiotics and prebiotics associated with aquaculture: a review. Fish & Shellfish Immunology, 45(2), 733-741.
Al-Dohail, M. A., Hashim, R., & Aliyu-Paiko, M. (2009). Effects of the probiotic, Lactobacillus acidophilus, on the growth performance, haematology parameters and immunoglobulin concentration in African Catfish (Clarias gariepinus, Burchell 1822) fingerling. Aquaculture Research, 40(14), 1642-1652.
Alexander, J. B., & Ingram, G. A. (1992). Noncellular nonspecific defence mechanisms of fish. Annual Review of Fish Diseases, 2, 249-279.
Al-Faragi, J.K., &Alsaphar, S.A. (2012). Isolation and Identification of Bacillus subtilus as Probiotic from Intestinal Microflora of Common Carp Cyprinus carpio L. In Proceeding of the Eleventh Veterinary Scientific Conference, 355, 361.
Aly, S. M., Abd-El-Rahman, A. M., John, G., & Mohamed, M. F. (2008). Characterization of some bacteria isolated from Oreochromis niloticus and their potential use as probiotics. Aquaculture, 277(1-2), 1-6.
Avendano, R. E., & Riquelme, C. E. (1999). Establishment of mixed culture probiotics and micro algae as food for bivalve larvae. Aquaculture Research, 30, 893–900. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1365- 2109.1999.00420.x
Balcazar, J. L. Blas, I. Zarzuela-Ruiz, I. Cunningham, D. Vendrell, D., & Múzquiz, J.L. (2007a). The role of probiotics in aquaculture (Review). Veterinary Microbiology, 114, 173–186.
Balcazar, J.L. Vendrell, D. Blas, I. Ruiz-Zarzuela, I. Gironés, O., & Múzquiz, J.L. (2007). In vitro competitive adhesion and production of antagonistic compounds by lactic acid bacteria against fish pathogens (Short communication). Veterinary Microbiology, 122, 373– 380. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.vetmic.2007.01.023
Bandyopadhyay, P., & Mohapatra P.K.D. (2009). Effect of a probiotic bacterium Bacillus circulans PB7 in the formulated diets: on growth, nutritional quality and immunity of Catla catla (Ham.). Fish Physiology and Biochemistry, 35, 467-478. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10695-008-9272-8
Bhatnagar, A., & Lamba, R. (2015). Antimicrobial Ability and Growth Promoting Effects of Feed Supplemented with Probiotic Bacterium Isolated from Gut Microflora of Cirrhinus mrigala. Journal of Integrative Agriculture, 14(3), 583-592.
Boyd, C.E. & Gross, A. (1998). Use of probiotics for improving soil and water quality in aquaculture ponds. In: T.W. Flegel (Ed.) Advances in shrimp biotechnology. National Center for Genetic Engineering and Biotechnology, Bangkok.
Cabello, F. C. (2006). Heavy use of prophylactic antibiotics in aquaculture: a growing problem for human and animal health and for the environment. Environmental Microbiology, 8(7), 1137-1144.
Carbone, D., & Faggio, C. (2016). Importance of prebiotics in aquaculture as immune stimulants. Effects on immune system of Sparus aurata and Dicentrarchus labrax. Fish & Shellfish Immunology, 54, 172-178.
Chang, C. I., & Liu, W. Y. (2002). An evaluation of two probiotic bacterial strains, Enterococcus faecium SF68 and Bacillus toyoi, for reducing edwardsiellosis in cultured European eel, Anguilla anguilla L. Journal of Fish Diseases, 25(5), 311-315.
Chaudhary, A., & Javed, I. Q. (2007). Influence of probiotic Pseudomonas pseudoalcaligenes fermented feed on growth performance of Rohu (Labeo rohita) fingerlings. Punjab University Journal of Zoology, 22(1-2), 41-56.
Cruz, P.M., Ibanez, A.L., Hermosillo, O.A.M., & Saad, H.C.R. (2012). Use of probiotics in aquaculture. ISRN Microbiology, https://doi.org/10.5402/2012/916845
Dalmin, G., Kathiresan, K., & Purushothaman, A. (2001). Effect of probiotics on bacterial population and health status of shrimp in culture pond ecosystem. Indian Journal of Experimental Biological, 39, 939-942.
Dalmo, R. A., Ingebrigtsen, K., & Bøgwald, J. (1997). Non-specific defense mechanisms in fish, with particular reference to the reticuloendothelial system (RES). Journal of Fish Diseases, 20(4), 241-273.
Das, A., Nakhro, K., Chowdhury, S., & Kamilya, D. (2013). Effects of potential probiotic Bacillus amyloliquifaciens FPTB16 on systemic and cutaneous mucosal immune responses and disease resistance of catla (Catla catla). Fish & Shellfish Immunology, 35(5), 1547-1553.
Dawood, M. A., & Koshio, S. (2016). Recent advances in the role of probiotics and prebiotics in carp aquaculture: a review. Aquaculture, 454, 243-251.
De, D., Ghoshal T.K., Pramanik, A., & Ganguly, S. (2009). Isolation, identification and methods of use of different beneficial microbes as probiotics in aquafeed. CIBA (ICAR) Spec. Publ. for Kakdwip Research Centre’s Training Manual on Brackishwater Aquaculture, 41, 173-175.
Dhanaraj, M., Haniffa, M. A., Singh, S. A., Arockiaraj, A. J., Ramakrishanan, C. M., Seetharaman, S., & Arthimanju, R. (2010). Effect of probiotics on growth performance of koi carp (Cyprinus carpio). Journal of Applied Aquaculture, 22(3), 202-209.
Dimitroglou, A., Merrifield, D. L., Carnevali, O., Picchietti, S., Avella, M., Daniels, C., Güroy, D., & Davies, S. J. (2011). Microbial manipulations to improve fish health and production a Mediterranean perspective. Fish & Shellfish Immunology, 30(1), 1-16.
Dohail, M. A., Hashim, R., & Aliyu-Paiko, M. (2009). Effects of the probiotic, Lactobacillus acidophilus, on the growth performance, haematology parameters and immunoglobulin concentration in African Catfish (Clarias gariepinus, Burchell 1822) fingerling. Aquaculture Research, 40(14), 1642-1652.
El-Haroun, E. R., & Goda, A. M. A. S., Chowdhury, M. A. K. (2006). Effect of dietary probiotic Biogens supplementation as a growth promoter on growth performance and feed utilization of Nile tilapia Oreochromis niloticus (L.). Aquaculture Research, 37, 1473-1480. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2109.2006.01584.x
Ellis, A. E. (1990). Lysozyme assays. Techniques in fish immunology, 1, 101-103.
Faramarzi, M. ,Jafaryan, H., Patimar, R., Iranshahi, F., Boloki, M.L., Farahi, A., Kiaalvandi, S., Ghamsary, M., Makhtoumi, N.M., & Iranshahi, F. (2011a). The effects of different concentrations of probiotic Bacillus sp. and different bio encapsulation times on growth performance and survival rate of Persian sturgeon (Acipencer persicus) larvae. World Journal of Fisheries and Marine Sciences, 3, 145–150.
Faramarzi, M., Kiaalvandi, S., & Iranshahi, F. (2011). The effect of probiotics on growth performance and body composition of common carp (Cyprinus carpio). Journal of Animal and Veterinary Advances, 10(18), 2408-2413.
Faramarzi, M., Kiaalvandi, S., Lashkarbolooki, M., & Iranshahi, F. (2011b). The investigation of Lactobacillus acidophilus as probiotics on growth performance and disease resistance of rainbow trout (Oncorhychus mykiss). American-Eurasian Journal of Scientific Research, 6, 32-38.
Fuller, R. (1989). A review: probiotics in man and animals. Journal of Applied Bacteriology, 66, 365–378.
Gatesoupe, F.J. (1999). The use of probiotics in aquaculture. Aquaculture, 180, 147–165. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0044-8486(99)00187-8
Gatesoupe, F.J. (2005). Probiotics and prebiotics for fish culture, at the parting of the ways. Aqua Feeds: Formulation & Beyond, 2, 3-5.
Gatlin, D. M. (2002) Nutrition and fish health. In: Fish Nutrition (ed. by J.E. Halver and R. W. Hardy), pp.671-702, Academic Press, San Diego, CA.
Ghosh, K., Sen, S. K., & Ray, A. K. (2003). Supplementation of an Isolated Fish Gut Bacterium, Bacillus subtilis, in Formulated Diets for Rohu, Labeo rohita, Fingerlings. The Israeli Journal of Aquaculture-Bamidgeh, 55(1), 13-12.
Gildberg, A., & Mikkelsen, H. (1998). Effects of supplementing the feed to Atlantic cod (Gadus morhua) fry with lactic acid bacteria and immuno-stimulating peptides during a challenge trial with Vibrio anguillarum. Aquaculture, 167(1-2), 103-113.
Gildberg, A., Mikkelsen, H., Sandaker, E., & Ringø, E. (1997). Probiotic effect of lactic acid bacteria in the feed on growth and survival of fry of Atlantic cod (Gadus morhua). Hydrobiologia, 352(1-3), 279-285.
Giri, S. S., Sukumaran, V., & Oviya, M. (2013). Potential probiotic Lactobacillus plantarum VSG3 improves the growth, immunity, and disease resistance of tropical freshwater fish, Labeo rohita. Fish & Shellfish Immunology, 34(2), 660-666.
Gohila R. (2013). Comparative Studies on Growth Performance of Probiotic Supplemented Rohu fingerlings. International Journal of Pharmaceutical and Biological Archives, 4(1), 84-88.
Gram, L., Melchiorsen, J., Spanggaard, B., Huber, I., & Nielsen, T. F. (1999). Inhibition of Vibrio anguillarum by Pseudomonas fluorescens AH2, a possible probiotic treatment of fish. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 65(3), 969-973.
Guerreiro, I., Oliva-Teles, A., & Enes, P. (2018). Prebiotics as functional ingredients: focus on Mediterranean fish aquaculture. Reviews in Aquaculture, 10(4), 800-832.
Gupta, A., Gupta, P., & Dhawan, A. (2014). Dietary supplementation of probiotics affects growth, immune response and disease resistance of Cyprinus carpio fry. Fish & Shellfish Immunology, 41(2), 113-119.
Harzeveli, A. R. S., Van Duffel, H., Dhert, P., Swings, J., & Sorgeloos, P. (1998). Use of a potential probiotic Lactococcus lactis AR21 strain for the enhancement of growth in the rotifer Brachionus plicatilis (Müller). Aquaculture Research, 29(6), 411-417.
Hassaan, M. S., El-Sayed, A. M. I., Mohammady, E. Y., Zaki, M. A. A., Elkhyat, M. M., Jarmolowicz, S., & El-Haroun, E.R. (2021). Eubiotic effect of a dietary potassium diformate (KDF) and probiotic (Lactobacillus acidophilus) on growth, hemato-biochemical indices, antioxidant status and intestinal functional topography of cultured Nile tilapia Oreochromis niloticus fed diet free fishmeal. Aquaculture, 533, 736147 https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquaculture.2020.736147
He, S., Wan, Q., Ren, P., Yang, Y., Yao, F., & Zhou, Z. (2011). The effect of dietary saccharoculture on growth performance, non-specific immunity and autochthonous gut microbiota of gibel carp Carassius auratus. Journal of Aquaculture Research and Development, 2(Special issue).
Hernandez, L. H. H., Barrera, T. C., Mejia, J. C., Mejia, G. C., Del Carmen, M., Dosta, M., & Sotres, J. A. M. (2010). Effects of the commercial probiotic Lactobacillus casei on the growth, protein content of skin mucus and stress resistance of juveniles of the Porthole livebearer Poecilopsis gracilis (Poecilidae). Aquaculture Nutrition, 16(4), 407-411.
Ige, B.A. (2013). Probiotic Use in Intensive Fish Farming. African Journal of Microbiology Research, 7(22), 2701-2711.
Irianto, A., & Austin, B. (2002). Use of Probiotics to Control Furunculosis in Rainbow Trout, Oncorhynchus mykiss (Walbaum). Journal of Fish Diseases, 25(6), 333-342.
Jaseera, K. V., Ebeneezar, S., Sayooj, P., Nair, A. V., & Kaladharan, P. (2021). Dietary supplementation of microalgae, Aurantiochytrium sp. and co-feeding with Artemia enhances the growth, stress tolerance and survival in Penaeus monodon (Fabricius, 1798) post larvae. Aquaculture, 533, 736176. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquaculture.2020.736176
Jorquera, M. A., Silva, F. R., & Riquelme, C. E. (2001). Bacteria in the culture of the scallop Argopecten purpuratus (Lamarck, 1819). Aquaculture International, 9, 285-303. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1020449324456
Kesarcodi-Watson, A., Kaspar, H., Lategan, M.J., & Gibson, L. (2008). Probiotics in aquaculture: the need, principles and mechanisms of action and screening processes. Aquaculture, 274, 1–14. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquaculture.2007.11.019
Lalloo, R., Ramchuran, S., Ramduth, D., Gorgens, J., & Gardiner, N. (2007). isolation and selection of bacillus spp. as potential biological agents for enhancement of water quality in culture of ornamental Fish. Journal of Applied Microbiology, 103(5), 1471-1479.
Lara-Flores, M. (2011). The use of probiotic in aquaculture: an overview. International Research Journal of Microbiology, 2(12), 471-478.
Lara-Flores, M., & Aguirre-Guzman, G. (2009). The use of probiotic in fish and shrimp aquaculture. A review. In: N.P. Guerra and L.P. Castro (Eds.) Probiotics: Production, evaluation and uses in animal feed. Research Signpost 37/661 (2), Fort P.O., Trivandrum-695 023, Kerala, India.
Lategan, M. J., Torpy, F. R., & Gibson, L. F. (2004). Control of saprolegniosis in the eel Anguilla australis Richardson, by Aeromonas media strain A199. Aquaculture, 240(1-4), 19-27.
Lilley, D. M., & Stillwell, R. J. (1965). Probiotics: growth promoting factors produced by micro-organisms. Science, 147, 747– 748. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.147.3659.747
Lin, S., Mao, S., Guan, Y., Luo, L., Luo, L., & Pan, Y. (2012). Effects of dietary chitosan oligosaccharides and Bacillus coagulans on the growth, innate immunity and resistance of koi (Cyprinus carpio koi). Aquaculture, 342, 36-41.
Mancuso, M. (2014). Probiotics in Aquaculture. Journal of Fisheries and Livestock Production.
Mohapatra, S., Chakraborty, T., Prusty, A.K., Das, P., Paniprasad, K., & Mohanta, K.N. (2012). Use of probiotics in the diet of rohu, Labeo rohita fingerlings: effects on growth nutrient digestibility, retention digestive enzyme activities and intestinal microflora. Aquaculture Nutrition, 18, 1-11. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2095.2011.00866.x
Munir, M. B., Hashim, R., Chai, Y. H., Marsh, T. L., & Nor, S. A. M. (2016). Dietary prebiotics and probiotics influence growth performance, nutrient digestibility and the expression of immune regulatory genes in snakehead (Channa striata) fingerlings. Aquaculture, 460, 59-68.
Nageswara, P.V., & Babu, D.E. (2006). Probiotics as an alternative therapy to minimize or avoid antibiotics use in aquaculture. Fishing Chimes, 26(1),112-114.
Nayak, S. K. (2010). Probiotics and immunity: a fish perspective. Fish & Shellfish Immunology, 29(1), 2-14.
Ouwehand, A.C., Salminen, S., & Isolauri, E. (2002). Probiotics: An Overview of Beneficial Effects. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek, 82(1-4), 279-289.
Panigrahi, A., & Azad, I. S. (2007). Microbial intervention for better fish health in aquaculture: The Indian scenario. Fish Physiology and Biochemistry, 33(4), 429-440.
Park, S. C., Shimamura, I., Fukunaga, M., Mori, K. I., & Nakai, T. (2000). Isolation of bacteriophages specific to a fish pathogen, Pseudomonas plecoglossicida, as a candidate for disease control. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 66(4), 1416-1422.
Prasad, L., Baghel, D. S., & Kumar, V. (2003). Role and prospects of probiotics use in aquaculture. Aquaculture, 4(2), 247-251.
Queiroz, J. F., & Boyd, C. E. (1998). Effects of a bacterial inoculum in channel catfish ponds. Journal of the World Aquaculture Society, 29(1), 67-73.
Raida, M. K., Larsen, J. L., Nielsen, M. E., & Buchmann, K. (2003). Enhanced resistance of rainbow trout, Oncorhynchus mykiss (Walbaum), against Yersinia ruckeri challenge following oral administration of Bacillus subtilis and B. licheniformis (BioPlus2B). Journal of Fish Diseases, 26(8), 495-498.
Rengpipat, S. (2005). Biocontrol of bacteria pathogens in aquaculture with emphasis on chage therapy. In: P. Walker, R. Lester and M.G. Bondad-Reantaso (Eds.). Diseases in Asian Aquaculture, 5, 543-552. Fish Health Section, Asian Fisheries Society, Manila.
Ringø, E., Olsen, R. E., Gifstad, T. Ø., Dalmo, R. A., Amlund, H., Hemre, G. I., & Bakke, A. M. (2010). Prebiotics in aquaculture: a review. Aquaculture Nutrition, 16(2), 117-136.
Sahoo, T. K., Jena, P. K., Nagar, N., Patel, A. K., & Seshadri, S. (2015). In-Vitro Evaluation of Probiotic Properties of Lactic Acid Bacteria from the Gut of Labeo rohita and Catla catla. Probiotics Antimicrobial Proteins, 7(2),126-136.
Sakai, M., Yoshida, T., Atsuta, S., & Kobayashi, M. (1995). Enhancement of resistance to vibriosis in rainbow trout, Oncorhynchus mykiss (Walbaum), by oral administration of Clostridium butyricum bacterin. Journal of Fish Diseases, 18(2), 187-190.
Salinas, I., Cuesta, A., Esteban, M. Á., & Meseguer, J. (2005). Dietary administration of Lactobacillus delbrüeckii and Bacillus subtilis, single or combined, on gilthead seabream cellular innate immune responses. Fish & Shellfish Immunology, 19(1), 67-77.
Son, V.M., Chang, C.C., Wu, M.C., Guu, Y.K., Chiu, C.H., & Cheng. W. (2009). Dietary administration of the probiotic, Lactobacillus plantarum, enhanced the growth, innate immune responses, and disease resistance of the grouper Epinephelus coioides. Fish & Shellfish Immunology, 26, 691-698. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fsi.2009.02.018
Spanggaard, B., Huber, I., Nielsen, J., Sick, E. B., Pipper, C. B., Martinussen, & Gram, L. (2001). The probiotic potential against vibriosis of the indigenous microflora of rainbow trout. Environmental Microbiology, 3(12), 755-765.
Suzer, C., Coban, D., Kamaci, H.O., Saka, S., Firat, K., Otgucuoglu, O., & Kucuksari, H. (2008). Lactobacillus spp. bacteria as probiotics in gilthead sea bream (Sparus aurata, L.) larvae: Effects on growth performance and digestive enzyme activities. Aquaculture, 280, 140-145. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquaculture.2008.04.020
Tacon, A. G., & Metian, M. (2013). Fish matters: importance of aquatic foods in human nutrition and global food supply. Reviews in Fisheries Science, 21(1), 22-38.
Taoka, Y., Maeda, H., Jo, J.Y., Jeon, M.J., Bai, S.C., Lee, W.J., Yuge, K., & Koshio, S., (2006). Growth, stress tolerance and non-specific immune response of Japanese flounder Paralichthys olivaceus to probiotics in a closed recirculating system. Fisheries Science, 72(2), 310-321.
Tuyet Hoa, T. T., Boerlage, A. S., My Duyen, T. T., Mai Thy, D. T., Thu Hang, N .T., Humprhy, R. W., Verschuere, L. Rombaut, G. Sorgeloos, P., & Verstraete, W. (2000). Probiotic bacteria as biological control agents in aquaculture. Microbiology and Molecular Biology Reviews, 64, 655-671. https://doi.org/10.1128/mmbr.64.4.655-671.2000
Vine, N.G., Leukes, W.D., Kaiser, H., Daya, S., Baxter, J., & Hecht, T. (2004). Competition for Attachment of Aquaculture Candidate Probiotic and Pathogenic Bacteria on Fish Intestinal Mucus. Journal of Fish Diseases, 27(6), 319-326.
Wang, Y. B., Li, J. R., & Lin, J. (2008). Probiotics in aquaculture: challenges and outlook. Aquaculture, 281(1-4), 1-4.
WHO. (2001). Health and Nutritional Properties of Probiotics in Food Including Powder Milk with Lactic Acid Bacteria. Medicine Report, 12(10), 328-330.
Wu, Z. X., Feng, X., Xie, L. L., Peng, X. Y., Yuan, J., & Chen, X. X. (2012). Effect of probiotic Bacillus subtilis Ch9 for grass carp, Ctenopharyngodon idella (Valenciennes, 1844), on growth performance, digestive enzyme activities and intestinal microflora. Journal of Applied Ichthyology, 28(5), 721-727.
Yilmaz, S., Yilmaz, E., Dawood, M. A. O., Ringo, E., Ahmadifar, E., & Abdel-Latif, H. M. R. (2022). Probiotics, prebiotics, and symbiotic used to control vibriosis in fish: a review. Aquaculture, 547, 737514. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquaculture.2021.737514
Yilmaz, S., Yilmaz, E., Dawood, M. A. O., Ringo, E., Ahmadifar, E., Abdel-Latif, H. M. R. (2022). Probiotics, prebiotics, and synbiotics used to control vibriosis in fish: a review. Aquaculture, 547, 737514 https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquaculture.2021.737514
Zhou, Q, Li, K., Jun, X., & Bo, L. (2009). Role and Functions of Beneficial Microorganisms in Sustainable Aquaculture. Bioresource Technology, 100(16), 3780-3786.
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2024 Agriculture and Environmental Science Academy

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.




