Factors affecting the adoption of farm mechanization in Rupandehi, Nepal
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.26832/24566632.2024.090301Keywords:
Chi-square, Custom hiring center, Index value, Mechanization, SubsidyAbstract
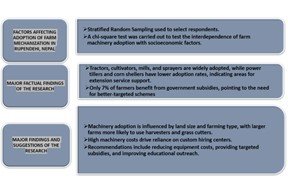
Agricultural mechanization is pivotal in farmer’s fields as it functions more efficiently and helps increase farm productivity. Despite the massive involvement of people in agriculture, farm productivity is relatively low. One main reason for this is the staggered implementation of farm mechanization. This paper aims to explore the factors affecting the adoption of farm mechanization using the Chi-square test and identify the major problems using relative frequency values. A total of 112 respondents, 28 each from 4 municipalities of Rupandehi district were interviewed based on stratified random sampling technique. The results showed that the adoption rates of various farm machinery were notably high, with tractors, cultivators, mills, and sprayers being universally employed by 93.75 % of the surveyed individuals. The government subsidies to only 7% of farmers facilitate machinery procurement. The size of the total cultivated land was found to be significant over the use of harvester, grass cutter, and power tiller, and owing of milling machine. The availability of subsidies and owning of mills were found inter dependent. The annual expenditures of farmers and their access to theCusto m Hiring Centre were found to be significant. Lastly, with index values of 0.402 and 0.393, the high costs of farm machinery and small land holdings were major problems in the adoption of farm mechanization. Therefore, addressing the high initial costs of modern farm equipment, providing targeted subsidies, innovative institution formation to provide better services to marginalized farmers, and expanding extension services are essential steps to promote the adoption of farm mechanization.
Downloads
References
Behrendt, K., & Paparas, D. (2020). Proceedings of the 3rd INFER Symposium on Agri-Tech Economics for Sustainable Futures.
Chi, Y., Zhou, W., Wang, Z., Hu, Y., & Han, X. (2021). The influence paths of agricultural mechanization on green agricultural development. Sustainability (Switzerland), 13(23). https://doi.org/10.3390/su132312984
Ghosh, B. K. (2010a). Determinants of Farm Mechanization in Modern Agriculture: A Case Study of Burdwan Districts of West Bengal. International Journal of Agricultural Research, 5(12), 1107–1115. https://doi.org/10.3923/ijar.2010.1107.1115
Ghosh, B. K. (2010b). Determinants of Farm Mechanization in Modern Agriculture: A Case Study of Burdwan Districts of West Bengal. International Journal of Agricultural Research, 5(12), 1107–1115. https://doi.org/10.3923/ijar.2010.1107.1115
Kalita, A. (2018). Factors Affecting Agricultural Mechanization in Assam. In International Journal of Research in Engineering, IT and Social Sciences (Vol. 08). http://indusedu.org
Kandel, S., Poudel, R., Saru, M. T., & Parajuli, T. (2021). Status of farm mechanization and its impact on maize production in Jhapa District, Nepal. Archives of Agriculture and Environmental Science, 6(3), 290–294. https://doi.org/10.26832/24566632.2021.060304
Namuth-Covert, D. M., Merk, H. L., & Haines, C. (2012). Chi-Square Test for Goodness of Fit in a Plant Breeding Example. Journal of Natural Resources and Life Sciences Education, 41(1), 22–22. https://doi.org/10.4195/jnrlse.2011.0014w
Nepal Rastra Bank Current Macroeconomic and Financial Situation of Nepal (Based on Annual Data of 2021/22) Real Sector. (n.d.).
Paudel, G. P., KC, D. B., Rahut, D. B., Khanal, N. P., Justice, S. E., & McDonald, A. J. (2019). Smallholder farmers’ willingness to pay for scale-appropriate farm mechanization: Evidence from the mid-hills of Nepal. Technology in Society, 59. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.techsoc.2019.101196
Peng, J., Zhao, Z., & Liu, D. (2022). Impact of Agricultural Mechanization on Agricultural Production, Income, and Mechanism: Evidence from Hubei Province, China. Frontiers in Environmental Science, 10. https://doi.org/10.3389/fenvs.2022.838686
Rasouli, F., Sadighi, H., & Minaei, S. (2009). Factors Affecting Agricultural Mechanization: A Case Study on Sunflower Seed Farms in Iran. International Journal of Agricultural Sciences and Technology, (Vol. 11). www.SID.ir
Shrestha, S. (n.d.). Status of Agricultural Mechanization in Nepal. www.unapcaem.org
Shrestha, S. (2022). An overview of agricultural mechanization in Nepal. In Kathmandu University Journal of Science, Engineering and Technology (Vol. 16, Issue 2).
Takeshima, H., Adhikari, R., & Kumar, A. (2015). Farm Household Typologies and Mechanization Patterns in Nepal Terai Descriptive Analysis of the Nepal Living Standards Survey Comprehensive Study of Dairy Sector in Assam View project Food Safety Project View project. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/308949890
Takeshima, H., & Liu, Y. (2020). Smallholder mechanization induced by yield-enhancing biological technologies: Evidence from Nepal and Ghana. Agricultural Systems, 184. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agsy.2020.102914
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2024 Agriculture and Environmental Science Academy

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.




