Integrated nutrient management improves the nutritional quality and yield of black rice
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.26832/24566632.2024.090306Keywords:
Black rice, Cow dung, Inorganic fertilizer, Protein, Starch, YieldAbstract
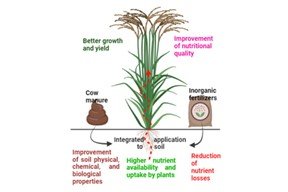
Integrated nutrient management combining inorganic and organic fertilizers is a promising approach to sustain crop production and soil health. As a premium rice type, integrated nutrients to cultivate black rice are rarely studied in Bangladesh. So, this research was conducted to identify the best combination of inorganic fertilizer (IF) and cow dung (CD) for maximizing the yield and nutritional quality of black rice. The experiment was conducted in the field laboratory of the Department of Agronomy, Bangladesh Agricultural University, Mymensingh following a Completely Randomized Design with four replications. Six treatments with single and combining IF and CD viz., 0% IF + 0% CD (IF0CD0), 100% IF + 0% CD (IF100CD0), 75% IF + 25% CD (IF75CD25), 50% IF + 50% CD (IF50CD50), 25% IF + 75% CD (IF25CD75), and 0% IF + 100% CD (IF0CD100) were applied. A significant variation was found among different treatments concerning plant growth, yield contributing characters, yield, and nutritional composition of black rice. Overall, a better performance was obtained from the application of 75% IF and 25% CD (IF75CD25) concerning most of the studied parameters with few deviations. The highest number of tillers hill-1(8.33), effective tillers hill-1 (7.33), panicle length (25.97 cm), spikelet’s panicle-1 (22.87), grains panicle-1 (129.7), grain yield (4 t ha-1), protein (9.71%), and potassium (0.58%) were found at the treatment IF75CD25. The overall results suggest that 25% cow dung combined with 75% recommended inorganic fertilizers can be applied to achieve maximum yield and nutritional quality of black rice in non-calcareous soil.
Downloads
References
Anisuzzaman, M., Rafii, M. Y., Jaafar, N. M., Izan Ramlee, S., Ikbal, M. F., & Haque, M. A. (2021). Effect of organic and inorganic fertilizer on the growth and yield components of traditional and improved rice (Oryza sativa L.) genotypes in Malaysia. Agronomy, 11(9), 1830. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy11091830
Asem, I. D., Imotomba, R. K., Mazumder, P. B., & Laishram, J. M. (2015). Anthocyanin content in the black scented rice (Chakhao): its impact on human health and plant defense. Symbiosis, 66, 47-54. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13199-015-0329-z
Bailey-Serres, J., Parker, J. E., Ainsworth, E. A., Oldroyd, G. E., & Schroeder, J. I. (2019). Genetic strategies for improving crop yields. Nature, 575(7781), 109-118. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-019-1679-0
Guo, J. H., Liu, X. J., Zhang, Y., Shen, J. L., Han, W. X., Zhang, W. F., & Zhang, F. S. (2010). Significant acidification in major Chinese croplands. Science, 327(5968), 1008-1010. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.11825
Guo, Z., Zhang, Z., Zhou, H., Wang, D., & Peng, X. (2019). The effect of 34-year continuous fertilization on the SOC physical fractions and its chemical composition in a Vertisol. Scientific reports, 9(1), 2505. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-019-38952-6
Huang, J., Huang, Z., Jia, X., Hu, R., & Xiang, C. (2015). Long-term reduction of nitrogen fertilizer use through knowledge training in rice production in China. Agricultural Systems, 135, 105-111. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agsy.2015.01.004
Iqbal, A., He, L., Khan, A., Wei, S., Akhtar, K., Ali, I., & Jiang, L. (2019). Organic manure coupled with inorganic fertilizer: An approach for the sustainable production of rice by improving soil properties and nitrogen use efficiency. Agronomy, 9(10), 651. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy9100651
Iqbal, A., Xie, H., He, L., Ahmad, S., Hussain, I., Raza, H., & Jiang, L. (2021). Partial substitution of organic nitrogen with synthetic nitrogen enhances rice yield, grain starch metabolism and related genes expression under the dual cropping system. Saudi Journal of Biological Sciences, 28(2), 1283-1296. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sjbs.2020.11.039
Jackson, M., 1973. Soil chemical analysis, pentice hall of India Pvt. Ltd., New Delhi, India 498, 151-154.
Kakar, K., Xuan, T. D., Noori, Z., Aryan, S., & Gulab, G. (2020). Effects of organic and inorganic fertilizer application on growth, yield, and grain quality of rice. Agriculture, 10(11), 544. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture10110544
Kumar, K. A., Swain, D. K., & Bhadoria, P. B. S. (2018). Split application of organic nutrient improved productivity, nutritional quality and economics of rice-chickpea cropping system in lateritic soil. Field Crops Research, 223, 125-136. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fcr.2018.04.007
Kumari, S., 2020. Black Rice: An emerging 'super food'. Pant Nagar Journal of Research, 18(1), 15-18.
Kushwaha, U. K. S. (2016). Black rice (pp. 21-47). Springer International Publishing. https://doi.org.10.1007/978-3-319-30153-2_2
Moe, K., Moh, S. M., Htwe, A. Z., Kajihara, Y., & Yamakawa, T. (2019). Effects of integrated organic and inorganic fertilizers on yield and growth parameters of rice varieties. Rice Science, 26(5), 309-318. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rsci.2019.08.005
Nashrurrokhman, M., Sayekti, P. R., Safitri, A., Purwestri, Y. A., & Pratiwi, R. (2019). Macronutrient and mineral contents of five local black rice (Oryza sativa) cultivars in Indonesia. Biodiversitas Journal of Biological Diversity, 20(12). https://doi.org/10.13057/biodiv/d201225
Page, A.L., Miller, R.H. & Keeny, D.R. (1982). Methods of Soil Analysis. Part-2: Chemical and Microbiological Properties (2nd edition.) American Society Agronomy Inc. Madison, Wisconsin, USA, pp. 252-255.
Peng, G. A. O., Zhang, T., Lei, X. Y., Cui, X. W., Lu, Y. X., Fan, P. F., & Zhang, H. M. (2023). Improvement of soil fertility and rice yield after long-term application of cow manure combined with inorganic fertilizers. Journal of Integrative Agriculture, 22(7), 2221-2232. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jia.2023.02.037
Rahman, M. R., Rahmana, M. R., Fazala, M. J., & Anwarb, M. P. (2020). Phenological Characterization and Yield Performance of Hilly Black Rice Cultivars Under Year-Round Cultivation in Plain Land Ecosystem of Bangladesh. Tropical Agrobiodiversity (TRAB), 1(2), 66-71. http://doi.org/10.26480/trab.02.2020.49.54
Raj, A., Jhariya, M. K., & Toppo, P. (2014). Cow dung for eco-friendly and sustainable productive farming. Environmental Science, 3(10), 201-202.
Subroto, E., Jeanette, G., Meiyanasari, Y., Luwinsky, I., & Baraddiaz, S. (2020). Review on the analysis methods of starch, amylose, amylopectinin food and agricultural products. International Journal of Emerging Trends in Engineering Research, 8(7). https://doi.org/10.30534/ijeter/2020/103872020
Sui, B., Feng, X., Tian, G., Hu, X., Shen, Q., & Guo, S. (2013). Optimizing nitrogen supply increases rice yield and nitrogen use efficiency by regulating yield formation factors. Field Crops Research, 150, 99-107. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fcr.2013.06.012
Suzuki, M., Kimura, T., Yamagishi, K., Shinmoto, H., Yamaki, K., 2004. Comparison of Mineral Contents in 8 Cultivars of Pigmented Brown Rice. Journal of the Japanese Society for Food Science and Technology, 51, 424-427. https://doi.org/10.3136/nskkk.51.424
Tandon, H. L. S. (2005). Methods of analysis of soils, plants, waters, fertilizers & organic manures. Fertiliser Development and Consultation Organisation. New Delhi- 110048, India.
Ton-ogan, M., & Bañoc, D. M. Response of Black, Red, and White Rice (Oryza sativa L.) Cultivars to Nutrient Management Under Highly Alkaline Soil. Science and Humanities Journal, 14(1). https://doi.org/10.47773/shj.1998.141.5
Wang, G., Chen, X., Cui, Z., Yue, S., & Zhang, F. (2014). Estimated reactive nitrogen losses for intensive maize production in China. Agriculture, Ecosystems & Environment, 197, 293-300. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agee.2014.07.014
Wang, J., Zhang, X., Yuan, M., Wu, G., & Sun, Y. (2023). Effects of partial replacement of nitrogen fertilizer with organic fertilizer on rice growth, nitrogen utilization efficiency and soil properties in the Yangtze river basin. Life, 13(3), 624. https://doi.org/10.3390/life13030624
Yang, D. S., Lee, K. S., Jeong, O. Y., Kim, K. J., & Kays, S. J. (2008). Characterization of volatile aroma compounds in cooked black rice. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 56(1), 235-240. https://doi.org/10.1021/jf072360c
Yuniarti, A., Machfud, Y., Damayani, M., & Solihin, E. (2019, December). The application of various types of organic fertilizer and N, P, K combination on soil fertility, growth and yield of black rice. In IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science (Vol. 393, No. 1, p. 012019). IOP Publishing. https://doi.org/10.1088/1755-1315/393/1/012019
Zhao, C., Hu, J., Li, Q., Fang, Y., Liu, D., Liu, Z., & Zhong, R. (2022). Transfer of nitrogen and phosphorus from cattle manure to soil and oats under simulative cattle manure deposition. Frontiers in Microbiology, 13, 916610. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2022.916610
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2024 Agriculture and Environmental Science Academy

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.




