A review on the impact of commonly used pesticides on the biology of earthworms
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.26832/24566632.2024.0904027Keywords:
Earthworm, Gut microbiota, Insecticide, Oxidative stress, PesticideAbstract
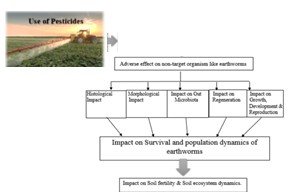
Earthworms are considered important bio-indicators of chemical contamination in the soil ecosystem. Being an important biotic factor of soil ecosystem, earthworms play a vital role in the functioning of soil ecosystems and maintenance of soil fertility. The present review encompasses the diverse effects of chemical contaminants like pesticides on earthworm biology, considering both direct toxicity and indirect impacts on ecosystem functions. Through a comprehensive review of existing literature, we assess the varying impacts of different classes of pesticides on earthworms. Several studies included in this review shed light on how pesticide exposure affects earthworm behaviour, reproduction, regenerative capacity, histology, gut microbial diversity, and nutrient transition, among other adverse effects, which consequently affect the soil ecosystem dynamics. Furthermore, we discuss the implications of these findings for agricultural practices, soil health, and biodiversity conservation. This study discusses the impact of pesticides on different facets of earthworm biology and emphasizes the necessity of sustainable pest management strategies to maintain the productivity and adaptability of ecosystems by enhancing our understanding of the complex interactions that occur between soil organisms, like earthworms, and foreign chemicals, or xenobiotics, like pesticides.
Downloads
References
Abdul, R. A., & Bouche, M. B. (1997). Earthworm toxicology: From acute to chronic tests. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 29(3-4), 699-703.
Ahmad, L., Khan, A., Khan, M. Z., Hussain, I., Mahmood, F., Sleemi, M. K., Lodhi, L. A., & Abdullah, I. (2012). Toxico-pathological effects of cypermethrin upon male reproductive system in rabbits. Pesticide Biochemistry and Physiology, 103(3), 194-201.
Ahmed, S. T. (2013). The impact of four pesticides on the earthworm Lumbricus terrestris (Annelida; Oligochaeta). International Journal of Current Research and Review, 5(21), 1.
Aina, P. O. (1984). Contribution of earthworms to porosity and water infiltration in a tropical soil under forest and long-term cultivation. Pedobiologia.
Alavanja, M. C. (2009). Introduction: Pesticides use and exposure, extensive worldwide. Reviews on Environmental Health, 24(4), 303-310.
Amenyogbe, E., Huang, J. S., Chen, G., & Wang, Z. (2021). An overview of the pesticides' impacts on fishes and humans. International Journal of Aquatic Biology, 9(1), 55-65.
Anjum, M. M., Ali, N., & Iqbal, S. (2017). Pesticides and environmental health: A review. Toxicology and Environmental Chemistry, 5, 555671.
Astaykina, A., Streletskii, R., Maslov, M., Krasnov, G., & Gorbatov, V. (2022). Effects of three pesticides on the earthworm Lumbricus terrestris gut microbiota. Frontiers in Microbiology, 13, 853535.
Bardiya, S., & Dixit, S. (2024). A review on effect of different pesticides on earthworm. International Journal of Science and Research Archive, 11(1), 590-599.
Bhadauria, T., & Saxena, K. G. (2010). Role of earthworms in soil fertility maintenance through the production of biogenic structures. Applied and Environmental Soil Science, 2010(1), 816073.
Bond, J. L., Kriesemer, S. K., Emborg, J. E., & Chadha, M. L. (2009). Understanding farmers' pesticide use in Jharkhand India. Extension Farming Systems Journal, 5(1), 53-61.
Booth, L. H., & O'Halloran, K. (2001). A comparison of biomarker responses in the earthworm Aporrectodea caliginosa to the organophosphorus insecticides diazinon and chlorpyrifos. Environmental Toxicology and Chemistry: An International Journal, 20(11), 2494-2502.
Booth, L. H., Heppelthwaite, V. J., & O'halloran, K. (2000). Growth development and fecundity of the earthworm Aporrectodea caliginosa after exposure to two organophosphates. New Zealand Plant Protection, 53, 221-225.
Bouché, M. B. (1977). Strategies lombriciennes. Ecological Bulletins, 122-132.
Brown, G. G., Benito, N. P., Pasini, A., Sautter, K. D., de F Guimarães, M., & Torres, E. (2003). No-tillage greatly increases earthworm populations in Paraná state, Brazil: The 7th international symposium on earthworm ecology· Cardiff· Wales· 2002. Pedobiologia, 47(5-6), 764-771.
Buchel, K. H. (Ed.). (1983). Chemistry of pesticides (pp. xii+-518).
Bustos-Obregón, E., & Goicochea, R. I. (2002). Pesticide soil contamination mainly affects earthworm male reproductive parameters. Asian Journal of Andrology, 4(3), 195-199.
Capowiez, Y., & Bérard, A. (2006). Assessment of the effects of imidacloprid on the behavior of two earthworm species (Aporrectodea nocturna and Allolobophora icterica) using 2D terraria. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 64(2), 198-206.
Capowiez, Y., Rault, M., Costagliola, G., & Mazzia, C. (2005). Lethal and sublethal effects of imidacloprid on two earthworm species (Aporrectodea nocturna and Allolobophora icterica). Biology and Fertility of Soils, 41(3), 135-143.
Casabé, N., Piola, L., Fuchs, J., Oneto, M. L., Pamparato, L., Basack, S., Giménez, R., Massaro, R., Papa, J. C., & Kesten, E. (2007). Ecotoxicological assessment of the effects of glyphosate and chlorpyrifos in an Argentine soya field. Journal of Soils and Sediments, 7, 232-239.
Chang, X., Sun, Y., Zhao, L., Li, X., Yang, S., Weng, L., & Li, Y. (2021). Exposure to fomesafen alters the gut microbiota and the physiology of the earthworm Pheretima guillelmi. Chemosphere, 284, 131290.
Cho, S. J., Cho, P. Y., Lee, M. S., Na, Y., Lee, J. H., Koh, K. S., Choo, J.K.,& Park, S. C. (2001). Up-regulation of multiple serine proteinases during earthworm tail regeneration. Invertebrate Reproduction & Development, 40(2-3), 103-108.
DasGupta, R., Chakravorty, P. P., & Kaviraj, A. (2012). Effects of carbaryl, chlorpyrifos and endosulfan on growth, reproduction and respiration of tropical epigeic earthworm, Perionyx excavatus (Perrier). Journal of Environmental Science and Health, Part B, 47(2), 99-103.
Datta, S., Singh, J., Singh, S., & Singh, J. (2016). Earthworms, pesticides and sustainable agriculture: a review. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 23(9), 8227-8243.
De Silva, P. M. C., Pathiratne, A., & van Gestel, C. A. (2010). Toxicity of chlorpyrifos, carbofuran, mancozeb and their formulations to the tropical earthworm Perionyx excavatus. Applied Soil Ecology, 44(1), 56-60.
Dittbrenner, N., Moser, I., Triebskorn, R., & Capowiez, Y. (2011). Assessment of short and long-term effects of imidacloprid on the burrowing behaviour of two earthworm species (Aporrectodea caliginosa and Lumbricus terrestris) by using 2D and 3D post-exposure techniques. Chemosphere, 84(10), 1349-1355.
Dittbrenner, N., Triebskorn, R., Moser, I., & Capowiez, Y. (2010). Physiological and behavioural effects of imidacloprid on two ecologically relevant earthworm species (Lumbricus terrestris and Aporrectodea caliginosa). Ecotoxicology, 19, 1567-1573.
Drake, H. L., & Horn, M. A. (2007). As the worm turns: the earthworm gut as a transient habitat for soil microbial biomes. Annual Review in Microbiology, 61(1), 169-189.
Edwards, C. A., & Bohlen, P. J. (1996). Biology and ecology of earthworms (Vol. 3). Springer Science & Business Media.
Espinoza‐Navarro, O., & Bustos‐Obregón, E. (2005). Effect of malathion on the male reproductive organs of earthworms, Eisenia foetida. Asian Journal of Andrology, 7(1), 97-101.
Faheem, M., & Khan, M. F. (2010). Toxicity of imidacloprid (Nicotinoid) against earthworm, Pheretima posthuma with reference to its effects on protein. Journal of Basic and Applied Science, 6(1), 55-62.
Ferreira, R. C., Papini, S., & de Andréa, M. M. (2015). Bioavailability and influence of 14C-carbofuran on Eisenia andrei avoidance, growth and reproduction in treated natural tropical soils. Journal of Environmental Science and Health, Part B, 50(4), 266-274.
Frampton, G. K., Jänsch, S., Scott‐Fordsmand, J. J., Römbke, J., & Van den Brink, P. J. (2006). Effects of pesticides on soil invertebrates in laboratory studies: a review and analysis using species sensitivity distributions. Environmental Toxicology and Chemistry: An International Journal, 25(9), 2480-2489.
Furlong, M. A., Singleton, D. R., Coleman, D. C., & Whitman, W. B. (2002). Molecular and culture-based analyses of prokaryotic communities from an agricultural soil and the burrows and casts of the earthworm Lumbricus rubellus. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 68(3), 1265-1279.
Gambi, N., Pasteris, A., & Fabbri, E. (2007). Acetylcholinesterase activity in the earthworm Eisenia andrei at different conditions of carbaryl exposure. Comparative Biochemistry and Physiology Part C: Toxicology & Pharmacology, 145(4), 678-685.
Gibbs, M. H., Wicker, L. F., & Stewart, A. J. (1996). A method for assessing sublethal effects of contaminants in soils to the earthworm, Eisenia foetida. Environmental Toxicology and Chemistry: An International Journal, 15(3), 360-368.
Gobi, M., & Gunasekaran, P. (2010). Effect of butachlor herbicide on earthworm Eisenia fetida—its histological perspicuity. Applied and Environmental Soil Science, 2010(1), 850758.
Gowri, S., & Thangaraj, R. (2020). Studies on the toxic effects of agrochemical pesticide (Monocrotophos) on physiological and reproductive behavior of indigenous and exotic earthworm species. International Journal of Environmental Health Research, 30(2), 212-225.
Greig-Smith, P. W. (1992). Ecotoxicology of Earthworms. Intercept.
Gupta, S. K., & Saxena, P. N. (2003). Carbaryl-induced behavioural and reproductive abnormalities in the earthworm Metaphire posthuma: a sensitive model. Alternatives to Laboratory Animals, 31(6), 587-593.
Hackenberger, D. K., Stjepanović, N., Lončarić, Ž., & Hackenberger, B. K. (2018). Acute and subchronic effects of three herbicides on biomarkers and reproduction in earthworm Dendrobaena veneta. Chemosphere, 208, 722-730.
Han, Y., Zhu, L., Wang, J., Wang, J., Xie, H., & Zhang, S. (2014). Integrated assessment of oxidative stress and DNA damage in earthworms (Eisenia fetida) exposed to azoxystrobin. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 107, 214-219.
Hole, D. G., Perkins, A. J., Wilson, J. D., Alexander, I. H., Grice, P. V., & Evans, A. D. (2005). Does organic farming benefit biodiversity? Biological Conservation, 122(1), 113-130.
Ibtissem, Z., Aicha, T., Nedjoud, G., Nawel, B., Houria, B., & Reda, D. M. (2012). Potential toxicity of an insecticide of the family of carbamates on a bio-indicator model of the pollution the earthworm Octodrilus complanatus (Oligochaeta, Lumbricidae). Annals of Biological Research, 3(11), 5367-5373.
Jeyanthi, V., Paul, J. A. J., Selvi, B. K., & Karmegam, N. (2016). Comparative study of biochemical responses in three species of earthworms exposed to pesticide and metal contaminated soil. Environmental Processes, 3, 167-178.
Jeyaprakasam, A., Muniyandi, B., James, A. J. P., Karmegam, N., & Ponnuchamy, K. (2021). Assessment of earthworm diversity and pesticide toxicity in Eudrilus eugeniae. Environmental Chemistry and Ecotoxicology, 3, 23-30.
Jordaan, M. S., Reinecke, S. A., & Reinecke, A. J. (2012). Acute and sublethal effects of sequential exposure to the pesticide azinphos-methyl on juvenile earthworms (Eisenia andrei). Ecotoxicology, 21, 649-661.
Kanedi, M. (2017). Inhibitory Effect of Carbofuran Furadan 3G on the Cocoon Production and Viability in Pheretima javanica Gates. IOSR Journal of Environmental Science, Toxicology and Food Technology, 11(5 Vers), 59-62.
Kanedi, M. (2017). Physiological effects of carbofuran on earthworm Pheretima javanica Gates. Advances in Life Sciences, 7(2), 21-25.
Kavitha, V., Anandhan, R., Alharbi, N. S., Kadaikunnan, S., Khaled, J. M., Almanaa, T. N., & Govindarajan, M. (2020). Impact of pesticide monocrotophos on microbial populations and histology of intestine in the Indian earthworm Lampito mauritii (Kinberg). Microbial Pathogenesis, 139, 103893.
Krishnaswamy, V. G., Jaffar, M. F., Sridharan, R., Ganesh, S., Kalidas, S., Palanisamy, V., & Mani, K. (2021). Effect of chlorpyrifos on the earthworm Eudrilus euginae and their gut microbiome by toxicological and metagenomic analysis. World Journal of Microbiology and Biotechnology, 37, 1-12.
Kumari, T., & Sinha, M. (2011). Effects of sublethal doses of Malthion on regeneration of earthworm D. willsi. The Ecoscan, 155-9.
Kuzyakov, Y., & Blagodatskaya, E. (2015). Microbial hotspots and hot moments in soil: concept & review. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 83, 184-199.
Lakhani, L. (2015). Impact of Dimethoate on brain of the earthworm Eudichogaster kinneari (Stephenson): A histological profile. Environment Conservation Journal, 16(1&2), 1-8.
Lammertyn, S., Masín, C. E., Zalazar, C. S., & Fernandez, M. E. (2021). Biomarkers response and population biological parameters in the earthworm Eisenia fetida after short term exposure to atrazine herbicide. Ecological Indicators, 121, 107173.
Lavelle, P., Barois, I., Martin, A., Zaidi, Z., & Schaefer, R. (1989). Management of earthworm populations in agro-ecosystems: a possible way to maintain soil quality? In Ecology of Arable Land—Perspectives and Challenges: Proceeding of an International Symposium, 9–12 June 1987 Swedish University of Agricultural Sciences, Uppsala, Sweden (pp. 109-122). Springer Netherlands.
Leena, L., Amrita, K., & Preeti, C. (2012). Effect of dimethoate on testicular histomorphology of the earthworm Eudichogaster Kinneari (Stephenson). International Research Journal of Biological Sciences, 1(4).
Li, M., Ma, X., Saleem, M., Wang, X., Sun, L., Yang, Y., & Zhang, Q. (2020). Biochemical response, histopathological change and DNA damage in earthworm (Eisenia fetida) exposed to sulfentrazone herbicide. Ecological Indicators, 115, 106465.
Lima, M. P., Cardoso, D. N., Soares, A. M., & Loureiro, S. (2015). Carbaryl toxicity prediction to soil organisms under high and low temperature regimes. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 114, 263-272.
Ling, H. (2006). Effect of Carbofuran on Protein Content and the SOD and TChE Activity of the Eisenia fetida Earthworm. Journal of Anhui Agricultural Science, 34, 3165.
Lister, L. J., Svendsen, C., Wright, J., Hooper, H. L., & Spurgeon, D. J. (2011). Modelling the joint effects of a metal and a pesticide on reproduction and toxicokinetics in Lumbricid earthworms. Environment International, 37(4), 663-670.
Liu, T., Liu, Y., Fang, K., Zhang, X., & Wang, X. (2020). Transcriptome, bioaccumulation and toxicity analyses of earthworms (Eisenia fetida) affected by trifloxystrobin and trifloxystrobin acid. Environmental Pollution, 265, 115100.
Liu, T., Wang, X., Chen, D., Li, Y., & Wang, F. (2018). Growth, reproduction and biochemical toxicity of chlorantraniliprole in soil on earthworms (Eisenia fetida). Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 150, 18-25.
Liu, T., Wang, X., You, X., Chen, D., Li, Y., & Wang, F. (2017). Oxidative stress and gene expression of earthworm (Eisenia fetida) to clothianidin. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 142, 489-496.
Lu, J., Wu, Q., Yang, Q., Li, G., Wang, R., Liu, Y., Duan, C., Duan, S., He, X., Huang, Z. and Peng, X., Yan, W., & Jiang, J. (2021). Molecular mechanism of reproductive toxicity induced by beta-cypermethrin in zebrafish. Comparative Biochemistry and Physiology Part C: Toxicology & Pharmacology, 239, 108894.
Lydy, M. J., & Linck, S. L. (2003). Assessing the impact of triazine herbicides on organophosphate insecticide toxicity to the earthworm Eisenia fetida. Archives of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 45, 343-349.
Ma, J., Cheng, C., Du, Z., Li, B., Wang, J., Wang, J., Wang, Z., & Zhu, L. (2019). Toxicological effects of pyraclostrobin on the antioxidant defense system and DNA damage in earthworms (Eisenia fetida). Ecological Indicators, 101, 111-116.
Mahmood, I., Imadi, S. R., Shazadi, K., Gul, A., & Hakeem, K. R. (2016). Effects of pesticides on environment. Plant, Soil and Microbes: Volume 1: Implications in Crop Science, 253-269.
Malla, M. A., Dubey, A., Kori, R. K., Sharma, V., Kumar, A., Yadav, S., & Kumari, S. (2023). GC–MS based untargeted metabolomics reveals the metabolic response of earthworm (Eudrilus eugeniae) after chronic combinatorial exposure to three different pesticides. Scientific Reports, 13(1), 8583.
Mandal, S., Chakravorty, P. P., & Kundu, J. K. (2017). Relative toxicity of two selected fungicides on acid phosphatase and alkaline phosphatase activity of epigeic earthworm Eisenia Fetida (Oligochaeta). World Wide J Multidis Res Develop/WWJMRD, 4, 14-17.
Mosleh, Y. Y., Ismail, S. M., Ahmed, M. T., & Ahmed, Y. M. (2003). Comparative toxicity and biochemical responses of certain pesticides to the mature earthworm Aporrectodea caliginosa under laboratory conditions. Environmental Toxicology: An International Journal, 18(5), 338-346.
Mosleh, Y. Y., Paris-Palacios, S., Couderchet, M., & Vernet, G. (2002). Biological effects of two insecticides on earthworms (Lumbricus terrestris L.) under laboratory conditions. Mededelingen (Rijksuniversiteit te Gent. Fakulteit van de Landbouwkundige en Toegepaste Biologische Wetenschappen), 67(2), 59-68.
Mosleh, Y. Y., Paris, Palacios, S., Couderchet, M., & Vernet, G. (2003). Acute and sublethal effects of two insecticides on earthworms (Lumbricus terrestris L.) under laboratory conditions. Environmental Toxicology: An International Journal, 18(1), 1-8.
Muangphra, P., Tharapoom, K., Euawong, N., Namchote, S., & Gooneratne, R. (2016). Chronic toxicity of commercial chlorpyrifos to earthworm Pheretima peguana. Environmental Toxicology, 31(11), 1450-1459.
Muthukaruppan, G., Janardhanan, S., & Vijayalakshmi, G. (2005). Sublethal Toxicity of the Herbicide Butachlor on the Earthworm Perionyx sansibaricus and its Histological Changes (5 pp). Journal of Soils and Sediments, 5, 82-86.
Nechitaylo, T. Y., Yakimov, M. M., Godinho, M., Timmis, K. N., Belogolova, E., Byzov, B. A., Kurakov, A. V., Jones, D. L., & Golyshin, P. N. (2010). Effect of the earthworms Lumbricus terrestris and Aporrectodea caliginosa on bacterial diversity in soil. Microbial Ecology, 59, 574-587.
Neuhauser, E. F., & Callahan, C. A. (1990). Growth and reproduction of the earthworm Eisenia fetida exposed to sublethal concentrations of organic chemicals. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 22(2), 175-179.
Nunes, M. E. T., Daam, M. A., & Espíndola, E. L. G. (2016). Survival, morphology and reproduction of Eisenia andrei (Annelida, Oligochaeta) as affected by Vertimec® 18 EC (ai abamectin) in tests performed under tropical conditions. Applied Soil Ecology, 100, 18-26.
Oluah, M. S., Obiezue, R. N. N., Ochulor, A. J., & Onuoha, E. (2010). Toxicity and histopathological effect of atrazine (herbicide) on the earthworm Nsukkadrilus mbae under laboratory conditions. Animal Research International, 7(3), 1287-1293.
Owagboriaye, F., Mesnage, R., Dedeke, G., Adegboyega, T., Aladesida, A., Adeleke, M., Owa, S., & Antoniou, M. N. (2021). Impacts of a glyphosate-based herbicide on the gut microbiome of three earthworm species (Alma millsoni, Eudrilus eugeniae and Libyodrilus violaceus): a pilot study. Toxicology Reports, 8, 753-758.
Panda, S., & Sahu, S. K. (2004). Recovery of acetylcholine esterase activity of Drawida willsi (Oligochaeta) following application of three pesticides to soil. Chemosphere, 55(2), 283-290.
Pawar, S. S., & Ahmad, S. (2014). Filter paper contact test method for estimation of toxic effect of chloropyriphose on earthworm, Eisenia fetida. International Research Journal of Science Engineering, 2(1), 23-25.
Qiao, Z., Li, P., Tan, J., Peng, C., Zhang, F., Zhang, W., & Jiang, X. (2022). Oxidative stress and detoxification mechanisms of earthworms (Eisenia fetida) after exposure to flupyradifurone in a soil-earthworm system. Journal of Environmental Management, 322, 115989.
Rani, L., Thapa, K., Kanojia, N., Sharma, N., Singh, S., Grewal, A. S., Srivastav, A. L., & Kaushal, J. (2021). An extensive review on the consequences of chemical pesticides on human health and environment. Journal of Cleaner Production, 283, 124657.
Rao, J. V., & Kavitha, P. (2004). Toxicity of azodrin on the morphology and acetylcholinesterase activity of the earthworm Eisenia foetida. Environmental Research, 96(3), 323-327.
Reddy, A. A., Reddy, M., & Mathur, V. (2024). Pesticide Use, Regulation, and Policies in Indian Agriculture. Sustainability, 16(17), 7839.
Reddy, N. C., & Rao, J. V. (2008). Biological response of earthworm, Eisenia foetida (Savigny) to an organophosphorous pesticide, profenofos. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 71(2), 574-582.
Reinecke, S. A., & Reinecke, A. J. (2007). The impact of organophosphate pesticides in orchards on earthworms in the Western Cape, South Africa. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 66(2), 244-251.
Ribera, D., Narbonne, J. F., Arnaud, C., & Saint-Denis, M. (2001). Biochemical responses of the earthworm Eisenia fetida andrei exposed to contaminated artificial soil, effects of carbaryl. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 33(7-8), 1123-1130.
Robidoux, P. Y., Svendsen, C., Caumartin, J., Hawari, J., Ampleman, G., Thiboutot, S., Weeks, J. M., & Sunahara, G. I. (2000). Chronic toxicity of energetic compounds in soil determined using the earthworm (Eisenia andrei) reproduction test. Environmental Toxicology and Chemistry: An International Journal, 19(7), 1764-1773.
Rodriguez-Campos, J., Dendooven, L., Alvarez-Bernal, D., & Contreras-Ramos, S. M. (2014). Potential of earthworms to accelerate removal of organic contaminants from soil: a review. Applied Soil Ecology, 79, 10-25.
Römbke, J., Garcia, M. V., & Scheffczyk, A. (2007). Effects of the fungicide benomyl on earthworms in laboratory tests under tropical and temperate conditions. Archives of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 53, 590-598.
Shi, Y., Shi, Y., Wang, X., Lu, Y., & Yan, S. (2007). Comparative effects of lindane and deltamethrin on mortality, growth, and cellulase activity in earthworms (Eisenia fetida). Pesticide Biochemistry and Physiology, 89(1), 31-38.
Singh, S., Singh, J., & Vig, A. P. (2016). Earthworm as ecological engineers to change the physico-chemical properties of soil: soil vs vermicast. Ecological Engineering, 90, 1-5.
Singh, S., Tiwari, R. K., & Pandey, R. S. (2020). An insight into the impact of triazophos and deltamethrin pesticides as individual and in combination on oxidative stress and histopathological alterations in Eudrilus eugeniae. Chemistry and Ecology, 36(2), 155-173.
Sinha, M. P., Srivastava, R., & Gupta, D. K. (2013). Earthworm biodiversity of Jharkhand: Taxonomic description. The Bioscan, 8(Supplement 1), 293-310.
Sorour, J., & Larink, O. (2001). Toxic effects of benomyl on the ultrastructure during spermatogenesis of the earthworm Eisenia fetida. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 50(3), 180-188.
Sujeeth, N. K., Aravinth, R., Thandeeswaran, M., Angayarkanni, J., Rajasekar, A., Mythili, R., & Gnanadesigan, M. (2023). Toxicity analysis and biomarker response of Quinalphos Organophosphate Insecticide (QOI) on eco-friendly exotic Eudrilus eugeniae earthworm. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 195(2), 274.
Taillebois, E., Cartereau, A., Jones, A. K., & Thany, S. H. (2018). Neonicotinoid insecticides mode of action on insect nicotinic acetylcholine receptors using binding studies. Pesticide Biochemistry and Physiology, 151, 59-66.
Tao, J., Rong, W., Diao, X., & Zhou, H. (2018). Toxic responses of Sox2 gene in the regeneration of the earthworm Eisenia foetida exposed to Retnoic acid. Comparative Biochemistry and Physiology Part C: Toxicology & Pharmacology, 204, 106-112.
Thompson, C. M., & Richardson, R. J. (2004). Anticholinesterase insecticides. In: Marrs, T. C., & Ballantyne, B. (Eds)Pesticide toxicology and international regulation. West Sussex, England: Wiley. p 89–127
Tiwari, R. K., Singh, S., & Pandey, R. S. (2019). Assessment of acute toxicity and biochemical responses to chlorpyrifos, cypermethrin and their combination exposed earthworm, Eudrilus eugeniae. Toxicology Reports, 6, 288-297.
Van Gestel, C. A. M. (1992). Validation of earthworm toxicity tests by comparison with field studies: a review of benomyl, carbendazim, carbofuran, and carbaryl. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 23(2), 221-236.
Velki, M., & Ečimović, S. (2015). Changes in exposure temperature lead to changes in pesticide toxicity to earthworms: a preliminary study. Environmental Toxicology and Pharmacology, 40(3), 774-784.
Velki, M., Hackenberger, B. K., Lončarić, Ž., & Hackenberger, D. K. (2014). Application of microcosmic system for assessment of insecticide effects on biomarker responses in ecologically different earthworm species. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 104, 110-119.
Wang, J. H., Zhu, L. S., Liu, W., Wang, J., & Xie, H. (2012). Biochemical responses of earthworm (Eisenia foetida) to the pesticides chlorpyrifos and fenvalerate. Toxicology Mechanisms and Methods, 22(3), 236-241.
Wang, J., Wang, J., Wang, G., Zhu, L., & Wang, J. (2016). DNA damage and oxidative stress induced by imidacloprid exposure in the earthworm Eisenia fetida. Chemosphere, 144, 510-517.
Wang, K., Pang, S., Mu, X., Qi, S., Li, D., Cui, F., & Wang, C. (2015). Biological response of earthworm, Eisenia fetida, to five neonicotinoid insecticides. Chemosphere, 132, 120-126.
Wang, K., Qi, S., Mu, X., Chai, T., Yang, Y., Wang, D., Li, D., Che, W., & Wang, C. (2015). Evaluation of the toxicity, AChE activity and DNA damage caused by imidacloprid on earthworms, Eisenia fetida. Bulletin of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 95, 475-480.
Wang, Y., Wu, S., Chen, L., Wu, C., Yu, R., Wang, Q., & Zhao, X. (2012). Toxicity assessment of 45 pesticides to the epigeic earthworm Eisenia fetida. Chemosphere, 88(4), 484-491.
Wu, R., Zhou, T., Wang, J., Wang, J., Du, Z., Li, B., Juhasz, A., & Zhu, L. (2021). Oxidative stress and DNA damage induced by trifloxystrobin on earthworms (Eisenia fetida) in two soils. Science of The Total Environment, 797, 149004.
Xiao, N., Jing, B., Ge, F., & Liu, X. (2006). The fate of herbicide acetochlor and its toxicity to Eisenia fetida under laboratory conditions. Chemosphere, 62(8), 1366-1373.
Xu, P., Diao, J., Liu, D., & Zhou, Z. (2011). Enantioselective bioaccumulation and toxic effects of metalaxyl in earthworm Eisenia foetida. Chemosphere, 83(8), 1074-1079.
Yao, X., Zhang, F., Qiao, Z., Yu, H., Sun, S., Li, X., Zhang, J., & Jiang, X. (2020). Toxicity of thifluzamide in earthworm (Eisenia fetida). Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 188, 109880.
Yasmin, S., & D’Souza, D. (2007). Effect of pesticides on the reproductive output of Eisenia fetida. Bulletin of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 79, 529-532.
Yasmin, S., & D′ Souza, D. (2010). Effects of pesticides on the growth and reproduction of earthworm: a review. Applied and Environmental soil science, 2010(1), 678360.
Yuan, Y., Teng, H., Zhang, T., Wang, D., Gu, H., & Lv, W. (2024). Toxicological effects induced by two carbamates on earthworms (Eisenia fetida): Acute toxicity, arrested regeneration and underlying mechanisms. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 269, 115824.
Zhang, C., Zhu, L., Wang, J., Wang, J., Du, Z., Li, B., Zhou, T., Cheng, C., & Wang, Z. (2018). Evaluating subchronic toxicity of fluoxastrobin using earthworms (Eisenia fetida). Science of the total environment, 642, 567-573.
Zhang, Q., Zhang, B., & Wang, C. (2014). Ecotoxicological effects on the earthworm Eisenia fetida following exposure to soil contaminated with imidacloprid. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 21, 12345-12353.
Zhang, Q., Zhu, L., Wang, J., Xie, H., Wang, J., Han, Y., & Yang, J. (2013). Oxidative stress and lipid peroxidation in the earthworm Eisenia fetida induced by low doses of fomesafen. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 20, 201-208.
Zhang, R., Zhou, Z., & Zhu, W. (2020). Evaluating the effects of the tebuconazole on the earthworm, Eisenia fetida by H-1 NMR-Based untargeted metabolomics and mRNA assay. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 194, 110370.
Zhang, X., Wang, X., Liu, Y., Fang, K., & Liu, T. (2020). The toxic effects of sulfoxaflor induced in earthworms (Eisenia fetida) under effective concentrations. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 17(5), 1740.
Zhao, S., Dong, J., Jeong, H. J., Okumura, K., & Ueda, H. (2018). Rapid detection of the neonicotinoid insecticide imidacloprid using a quenchbody assay. Analytical and bioanalytical chemistry, 410, 4219-4226.
Zhou, Q. X., Zhang, Q. R., & Liang, J. D. (2006). Toxic effects of acetochlor and methamidophos on earthworm Eisenia fetida in phaiozem, northeast China. Journal of Environmental Sciences, 18(4), 741-745.
Zhou, S. P., Duan, C. Q., Hui, F. U., Chen, Y. H., Wang, X. H., & Yu, Z. F. (2007). Toxicity assessment for chlorpyrifos-contaminated soil with three different earthworm test methods. Journal of Environmental Sciences, 19(7), 854-858.
Zhu, L., Li, B., Wu, R., Li, W., Wang, J., Wang, J., Du, Z., Juhasz, A., & Zhu, L. (2020). Acute toxicity, oxidative stress and DNA damage of chlorpyrifos to earthworms (Eisenia fetida): The difference between artificial and natural soils. Chemosphere, 255, 126982.
Zoran, M. J., Heppner, T. J., & Drewes, C. D. (1986). Teratogenic effects of the fungicide benomyl on posterior segmental regeneration in the earthworm, Eisenia fetida. Pesticide science, 17(6), 641-652.
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2024 Agriculture and Environmental Science Academy

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.




