Nutrient management with cow dung and chemical fertilizers enhances leaf yield and gel constituents in Aloe vera
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.26832/24566632.2025.1003019Keywords:
Aloe vera, Gel yield, Nutrient concentrations, Inorganic fertilizers, Integrated nutrient managementAbstract
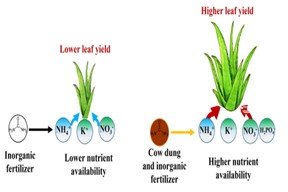
Since ancient times, Aloe vera has been used extensively, including in the cosmetics and food businesses. Commercial cultivation of A. vera is scarce due to lack of information. Therefore, a field experiment was conducted to examine the integrated effect of inorganic fertilizer (IF) and cow dung (CD) on the growth, yield, and nutritional composition of A. vera. A randomized complete block design (RCBD) with four replications was used for the experiment having total nine treatment combinations of IF and CD viz., IF 0% + CD 0%, IF 100% + CD 0%, IF 75% + CD 25%, IF 50% + CD 50%, IF 40% + CD 60%, IF 30% + CD 70%, IF 20% + CD 80%, IF 10% + CD 90%, and IF 0% + CD 100%. Varying combinations of IF and CD significantly influenced the studied parameters. On average, applications of 30% IF and 70% CD enhanced the leaf yield by 37%, gel yield by 31% and nutritional quality by 28% compared to control. The post-harvest soil characteristics, including the percentage of nitrogen and organic matter, soil pH, exchangeable potassium, available phosphorus, and available sulfur, were found to increase with the higher application of cow dung. Applying both 30% IF and 70% CD showed a substantial increase in growth, yield, gel nutritional quality, and post-harvest soil characteristics compared to other treatments including control. Therefore, application of 30% IF with 70% CD could be a best strategy for obtaining improved growth, yield, and nutritional quality of A. vera.
Downloads
References
Aćin, V., Mirosavljević, M., Živančev, D., Jocković, B., Brbaklić, L., & Jaćimović, G. (2023). Field management practices to produce nutritional and healthier main crops. In Developing Sustainable and Health Promoting Cereals and Pseudocereals (pp. 137-173). Academic Press. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-323-90566-4.00006-0
Ahmad, M. A., Gupta, L. M., & Gupta, M. (2016). Effect of integrated nutrient management on growth and yield of Aloe barbadensis. The Indian Journal of Agricultural Sciences, 86, 91-95. https://doi.org/10.56093/ijas.v86i1.55236
Bader, B. R., Taban, S. K., Fahmi, A. H., Abood, M. A., & Hamdi, G. J. (2021). Potassium availability in soil amended with organic matter and phosphorous fertiliser under water stress during maize (Zea mays L) growth. Journal of the Saudi Society of Agricultural Sciences, 20(6), 390-394. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jssas.2021.04.006
Bai, Y., Niu, Y., Qin, S., & Ma, G. (2023). A new biomaterial derived from Aloe vera-Acemannan from basic studies to clinical application. Pharmaceutics, 15(7), 1913. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics15071913
Barłóg, P. (2023). Improving fertilizer use efficiency-methods and strategies for the future. Plants, 12(20), 3658. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants12203658
Black, C. A. (1958). Soil-plant relationships. Soil Science, 85(3), 175. https://journals.lww.com/soilsci/citation/1958/03000/Soil_Plant_Relationships.23.aspx
Chen, M., Zhang, S., Liu, L., Wu, L., & Ding, X. (2021). Combined organic amendments and mineral fertilizer application increase rice yield by improving soil structure, P availability and root growth in saline-alkaline soil. Soil and Tillage Research, 212, 105060. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.still.2021.105060
Chowdhury, M. A. H., Rahman, M. R., Billah, M., & Saha, B. K. (2024). Integrated nutrient management improves the nutritional quality and yield of black rice. Archives of Agriculture and Environmental Science, 9(3), 442-448. https://doi.org/10.26832/24566632.2024.090306
Chowdhury, M. A. H., Sultana, T., Rahman, M. A., Chowdhury, T., Enyoh, C. E., Saha, B. K., & Qingyue, W. (2020). Nitrogen use efficiency and critical leaf N concentration of Aloe vera in urea and diammonium phosphate amended soil. Heliyon, 6(12). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.heliyon.2020.e05718
Chowdhury, T., Chowdhury, M. A. H., Qingyue, W., Enyoh, C. E., Wang, W., & Khan, M. S. I. (2021). Nutrient uptake and pharmaceutical compounds of Aloe vera as influenced by integration of inorganic fertilizer and poultry manure in soil. Heliyon, 7(7). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.heliyon.2021.e07464
Darzi, S., Paul, K., Leitan, S., Werkmeister, J. A., & Mukherjee, S. (2021). Immunobiology and application of aloe vera-based scaffolds in tissue engineering. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 22(4), 1708. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22041708
Fang, H., Baret, F., Plummer, S., & Schaepman‐Strub, G. (2019). An overview of global leaf area index (LAI): Methods, products, validation, and applications. Reviews of Geophysics, 57(3), 739-799. https://doi.org/10.1029/2018RG000608
Gayithri, H. N., Jayaprasad, K. V., & Narayanaswamy, P. (2004). Response of bio-fertilizers and their combined application with different, levels of inorganic fertilizers in statice (Lumonuan Caspia). Journal of Ornamental Horticulture, 7(1), 70-74.
Ghosh, A., Bajaj, J., Hasan, R. & Singh, D. (1983). Soil and Water Testing Methods: A Laboratory Manual. IARI: New Delhi.
Gomez, K. A. & A. A. Gomez. (1984). Statistical Procedures for Agricultural Research. John Wiley & Sons.
Hasan, M. N., Bari, M. A. & Lutfar, M. R. (2020). Soil fertility trends in Bangladesh 2010 to 2020. SRSRF project. Soil Resource Development Institute, Ministry of Agriculture: Dhaka, Bangladesh, pp. 58–66.
Hoque, T. S., Hasan, A. K., Hasan, M. A., Nahar, N., Dey, D. K., Mia, S., & Kader, M. A. (2022). Nutrient release from vermicompost under anaerobic conditions in two contrasting soils of Bangladesh and its effect on wetland rice crop. Agriculture, 12(3), 376. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture12030376
Hossain, A. M. D. (2022). Production of Aloe vera under Integrated Fertilization of Inorganic Fertilizer and Cow Dung. Proceedings of the Workshop of Bangladesh Agricultural University Research Progress Workshops, Bangladesh 33, 136.
Hu, W., Zhang, Y., Xiangmin, R., Fei, J., Peng, J., & Luo, G. (2023). Coupling amendment of biochar and organic fertilizers increases maize yield and phosphorus uptake by regulating soil phosphatase activity and phosphorus-acquiring microbiota. Agriculture, Ecosystems & Environment, 355, 108582. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agee.2023.108582
Huang, L. M., Jia, X. X., Zhang, G. L., & Shao, M. A. (2017). Soil organic phosphorus transformation during ecosystem development: A review. Plant and Soil, 417(1), 17-42. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-017-3240-y
Huq, S. I., & Shoaib, J. M. (2013). The soils of Bangladesh (Vol. 1). Dordrecht: Springer. https://link.springer.com/series/8915
Jackson, M. (1973). Soil Chemical Analysis. Prentice Hall of India Pvt. Ltd.: New Delhi, India, Vol. 498.
Khaim, S., Chowdhury, M. A. H., & Saha, B. K. (2014). Organic and inorganic fertilization on the yield and quality of soybean. Journal of the Bangladesh Agricultural University, 11(1), 23-28. https://doi.org/10.3329/jbau.v11i1.18199
Khan, K. S., Ali, M. M., Naveed, M., Rehmani, M. I. A., Shafique, M. W., Ali, H. M., & Feng, G. (2022). Co-application of organic amendments and inorganic P increase maize growth and soil carbon, phosphorus availability in calcareous soil. Frontiers in Environmental Science, 10, 949371. https://doi.org/10.3389/fenvs.2022.949371
Liu, Y., Lan, X., Hou, H., Ji, J., Liu, X., & Lv, Z. (2024). Multifaceted ability of organic fertilizers to improve crop productivity and abiotic stress tolerance: Review and perspectives. Agronomy, 14(6), 1141. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy14061141
Maan, A. A., Nazir, A., Khan, M. K. I., Ahmad, T., Zia, R., Murid, M., & Abrar, M. (2018). The therapeutic properties and applications of Aloe vera: A review. Journal of herbal medicine, 12, 1-10. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.hermed.2018.01.002
Manjhi, R. P., M. S. Yadava, and R. Thakur. (2014). Effect of integrated nutrient management on crop productivity and changes in soil fertility in maize (Zea mays)-wheat (Triticum aestivum) cropping sequence. Indian Journal of Agronomy, 59 (3), 371-376. https://doi.org/10.59797/ija.v59i3.5610
Page, A., Miller A. & Keeny, D. (1982). Methods of Soil Analysis. In Chemical and microbiological methods. American Society of Agronomy, Inc.: Madison, Wisconsin, USA.
Pahalvi, H. N., Rafiya, L., Rashid, S., Nisar, B., & Kamili, A. N. (2021). Chemical fertilizers and their impact on soil health. In Microbiota and biofertilizers, Vol 2: Ecofriendly tools for reclamation of degraded soil environs (pp. 1-20). Cham: Springer International Publishing. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-61010-4_1
Paul, T., Saha, B. K., Mohiuddin, K. M., Debi, M. R., & Uddin, M. K. (2023). Enhanced efficiency organo-mineral fertilizer improves yield and quality of red amaranth. Journal of Science and Technology Research, 5(1), 37-44. https://doi.org/10.3329/jscitr.v5i1.73995
Priya, E., Sarkar, S., & Maji, P. K. (2024). A review on slow-release fertilizer: Nutrient release mechanism and agricultural sustainability. Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering, 12(4), 113211. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2024.113211
Rashid, H. (2023). Problem and Prospect of Pharmaceuticals Industry of Bangladesh amid LDC Graduation. South Asian Journal of Social Studies and Economics, 20(4), 173-188. https://doi.org/10.9734/sajsse/2023/v20i4751
Reganold, J. P., & Wachter, J. M. (2016). Organic agriculture in the twenty-first century. Nature Plants, 2(2), 1-8. https://doi.org/10.1038/nplants.2015.221
Roba, T. B. (2018). Review on: The effect of mixing organic and inorganic fertilizer on productivity and soil fertility. Open Access Library Journal, 5(06), 4618. https://doi.org/10.4236/oalib.1104618
Sánchez, M., González-Burgos, E., Iglesias, I., & Gómez-Serranillos, M. P. (2020). Pharmacological update properties of Aloe vera and its major active constituents. Molecules, 25(6), 1324. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25061324
Sheoran, H. S., Duhan, B. S., Grewal, K. S., & Sheoran, S. (2015). Grain yield and NPK uptake of wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) as influenced by nitrogen, vermicompost and herbicide (Clodinafop propargyl). African Journal of Agricultural Research, 10(42), 3952-3961. https://doi.org/10.5897/AJAR2015.9918
Simi, F., & Hossain, M. J. (2023). Impact of fertilizer sources, both organic and inorganic, on Aloe. International Journal, 4(01), 82-86. https://doi.org/10.18801/ijmp.040123.13
Sultana, T., Chowdhury, M. A. H., Saha, B. K., Rahman, A., Chowdhury, T., & Sultana, R. (2021). Response of Aloe vera to potassium fertilization in relation to leaf biomass yield, its uptake and requirement, critical concentration and use efficiency. Journal of Plant Nutrition, 44(14), 2081-2095. https://doi.org/10.1080/01904167.2021.1881546
Tandon, H. (2005). Methods of Analysis of Soil Plant Water and Fertilizer, 2nd ed. Fertiliser Development and Consultation Organisation: New Delhi.
Uddin, M. J., Hooda, P. S., Mohiuddin, A. S. M., Haque, M. E., Smith, M., Waller, M., & Biswas, J. K. (2022). Soil organic carbon dynamics in the agricultural soils of Bangladesh following more than 20 years of land use intensification. Journal of Environmental Management, 305, 114427. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2021.114427
Usman, R. B., Adamu, M., Isyaku, I. M., & Bala, H. A. (2020). Quantitative and qualitative phytochemicals and proximate analysis of Aloe vera (Aloe barbadensis miller). International Journal of Advanced Academic Research Sciences Technology and Engineering, 6(1). https://doi.org/0.13140/RG.2.2.16689.12643
Viyasan, A., Sutharsan, S., & Srikrishnah, S. (2022). Growth and Yield of Aloe vera in Response to Different Organic Fertilizers or Manures. Journal of Agro-Technology and Rural Sciences, 2(1). https://doi.org/10.4038/atrsj.v2i1.37
Yu, Z., Guo, B., Sun, T., Li, R., Zhao, Z., & Yao, L. (2025). Effects of organic fertilizer substitution for mineral fertilizer on soil fertility, yield, and quality of muskmelons. Agronomy, 15(3), 639. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15030639
Zaman, M. M., Chowdhury, M. A. H., Islam, M. R., & Uddin, M. R. (2015). Effects of vermicompost on growth and leaf biomass yield of stevia and post harvest fertility status of soil. Journal of the Bangladesh Agricultural University, 13(2), 169-174. https://doi.org/10.22004/ag.econ.235277
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Agriculture and Environmental Science Academy

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.




