Effect of municipal solid waste compost and NPK fertilizer on growth, yield and protein content of rice (cv. BRRI dhan49)
Abstract
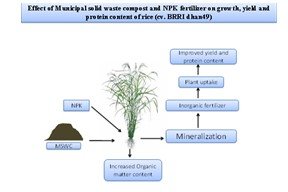
An experiment was conducted to study the effect of municipal solid waste compost (MSWC) on growth, yield and protein content as well as to know the effect of combined application of MSWC and NPK fertilizers in rice (cv. BRRI dhan49). There were six treatments including- T0 = Control (No fertilizer or no MSWC); T1= 100% Recommended Doses of Fertilizers (RDF) NPK; T2 = (MSWC @ 5 t ha-1+ 75% RDF); T3= (MSWC @ 7. 5t ha-1+ 50% RDF); T4= (MSWC @ 10 t ha-1 + 25% RDF); T5 = (MSWC @ 10 t ha-1). The experiment was laid out in a randomized complete block design (RCBD) with three replications. Our results showed that the integrated application of MSWC and different RDF% had a significant impact on various plant growth and yield parameters including plant height, panicle length, number of effective tillers per hill, number of filled grains per panicle, 1000-grain weight (g), and grain and straw yield of rice. In case of T2 treatment, highest grain yield (5.70 t ha-1), straw yield (7.71 t ha-1) and protein
content (5.875%) were obtained. Thus, the result indicated that combined application of MSWC with NPK performed better than the single application of either MSWC or NPK fertilizer.
Keywords:
MSWC, Protein content, NPK fertilizer, Rice, Yield parametersDownloads
References
Aktar, S. A. L. M. A., Islam, M. S., Hossain, M. S., Akter, H., Maula, S., & Hossain, S. S. F. (2018). Effects of municipal solid waste compost and fertilizers on the biomass production and yield of BRRI dhan 50. Progressive Agriculture, 29(2), 82-90.
BBS (Bangladesh Bureau of Statistics). (2019). Yearly Statistical Bulletin, Statistical Year Book of Bangladesh. Stat. Div., Ministry Planning, Govt. People’s Repub. Bangldesh. P. 39.
Black, C.A. (1965). Method of Soil Analysis, Part 2, Chemical and Microbiological Properties; American Society of Agronomy, Inc.: Madison, WI, USA.
Bremner, J. M., & Mulvaney, C. S. (1982). Nitrogen-Total. In Methods of Soil Analysis, Part 2; Page, A.L., Miller, R.H., Keeney, D.R., Eds.; ASA & SSSA: Madison, WI, USA, pp. 595–624.
Fox, R. L., Olson, R. A., & Rhoades, H. F. (1964). Evaluating the sulfur status of soils by plants and soil tests. Soil Science Society of American Journal, 28, 243–246.
Kumar, A. K., Rao S. K., Devi U. M., & Kumar, S. D. (2019). Yield and Water Productivity Response of Rice to Application of urban compost. (2019). International Journal of Current Microbiology and Applied Sciences, 8(12), 1872-1878.
Moe, K., Moh, S. M., Htwe, A. Z., Kajihara, Y., & Yamakawa, T. (2019). Effects of integrated organic and inorganic fertilizers on yield and growth parameters of rice varieties. Rice Science, 26(5), 309-318.
Olsen, S. R. (1982). Phosphorus. Methods of soil analysis, 2, 403-430.
Peech, M. (1965). Hydrogen‐ion activity. Methods of Soil Analysis: Part 2 Chemical and Microbiological Properties, 9, 914-926.
Rajaie, M., & Tavakoly, A. R. (2016). Effects of municipal waste compost and nitrogen fertilizer on growth and mineral composition of tomato. International Journal of Recycling of Organic Waste in Agriculture, 5(4), 339-347.
Salam, A. A., Ashrafuzzaman, M., Sikder, S., Mahmud, A., & Joardar, J. C. (2021). Influence of municipal solid waste compost on yield of tomato-applied solely and in combination with inorganic fertilizer where nitrogen is the only variable factor. Malaysian Journal of Sustainable Agriculture (MJSA), 5(1), 29-33.
Sarkar, S. K., Paul, S. K., Saha, K. K., Baroi, A., & Sarkar, M. A. R. (2021). Impact of vermicompost based nitrogen management and plant spacing on the performance of short duration transplant Aus rice (cv. Parija). Archives of Agriculture and Environmental Science, 6(4), 542-547.
Scotti, R., Pane, C., Spaccini, R., Palese, A. M., Piccolo, A., Celano, G., & Zaccardelli, M. (2016). On-farm compost: a useful tool to improve soil quality under intensive farming systems. Applied Soil Ecology, 107, 13-23.
Sultana, M., Jahiruddin, M., Islam, M. R., Rahman, M. M., Abedin, M. A., & Solaiman, Z. M. (2021). Nutrient enriched municipal solid waste compost increases yield, nutrient content and balance in rice. Sustainability, 13(3), 1047.
Srivastava, V., De Araujo, A. S. F., Vaish, B., Bartelt-Hunt, S., Singh, P., & Singh, R. P. (2016). Biological response of using municipal solid waste compost in agriculture as fertilizer supplement. Reviews in Environmental Science and Bio/Technology, 15(4), 677-696.
Yogananda, S. B., Parama, V. R., Prakash, S. S., & Thimmegowda, M. N. (2019). Effect of biodegradable urban waste compost on growth and yield of maize (Zea mays L.). Indian Journal of Agricultural Research, 53(6).
Aktar, S. A. L. M. A., Islam, M. S., Hossain, M. S., Akter, H., Maula, S., & Hossain, S. S. F. (2018). Effects of municipal solid waste compost and fertilizers on the biomass production and yield of BRRI dhan 50. Progressive Agriculture, 29(2), 82-90.
BBS (Bangladesh Bureau of Statistics). (2019). Yearly Statistical Bulletin, Statistical Year Book of Bangladesh. Stat. Div., Ministry Planning, Govt. People’s Repub. Bangldesh. P. 39.
Black, C.A. (1965). Method of Soil Analysis, Part 2, Chemical and Microbiological Properties; American Society of Agronomy, Inc.: Madison, WI, USA.
Bremner, J. M., & Mulvaney, C. S. (1982). Nitrogen-Total. In Methods of Soil Analysis, Part 2; Page, A.L., Miller, R.H., Keeney, D.R., Eds.; ASA & SSSA: Madison, WI, USA, pp. 595–624.
Fox, R.L., Olson, R.A. and Rhoades, H.F. (1964). Evaluating the sulfur status of soils by plants and soil tests. Soil Science Society of American Journal, 28, 243–246.
Kumar, A. K., Rao S. K., Devi U. M., & Kumar, S. D. (2019). Yield and Water Productivity Response of Rice to Application of urban compost. (2019). International Journal of Current Microbiology and Applied Sciences, 8(12), 1872-1878.
Moe, K., Moh, S. M., Htwe, A. Z., Kajihara, Y., & Yamakawa, T. (2019). Effects of integrated organic and inorganic fertilizers on yield and growth parameters of rice varieties. Rice Science, 26(5), 309-318.
Olsen, S. R. (1982). Phosphorus. Methods of soil analysis, 2, 403-430.
Peech, M. (1965). Hydrogen‐ion activity. Methods of Soil Analysis: Part 2 Chemical and Microbiological Properties, 9, 914-926.
Rajaie, M., & Tavakoly, A. R. (2016). Effects of municipal waste compost and nitrogen fertilizer on growth and mineral composition of tomato. International Journal of Recycling of Organic Waste in Agriculture, 5(4), 339-347.
Salam, A. A., Ashrafuzzaman, M., Sikder, S., Mahmud, A., & Joardar, J. C. (2021). Influence of municipal solid waste compost on yield of tomato-applied solely and in combination with inorganic fertilizer where nitrogen is the only variable factor. Malaysian Journal of Sustainable Agriculture (MJSA), 5(1), 29-33.
Sarkar, S. K., Paul, S. K., Saha, K. K., Baroi, A., & Sarkar, M. A. R. (2021). Impact of vermicompost based nitrogen management and plant spacing on the performance of short duration transplant Aus rice (cv. Parija). Archives of Agriculture and Environmental Science, 6(4), 542-547.
Scotti, R., Pane, C., Spaccini, R., Palese, A. M., Piccolo, A., Celano, G., & Zaccardelli, M. (2016). On-farm compost: a useful tool to improve soil quality under intensive farming systems. Applied Soil Ecology, 107, 13-23.
Sultana, M., Jahiruddin, M., Islam, M. R., Rahman, M. M., Abedin, M. A., & Solaiman, Z. M. (2021). Nutrient enriched municipal solid waste compost increases yield, nutrient content and balance in rice. Sustainability, 13(3), 1047.
Srivastava, V., De Araujo, A. S. F., Vaish, B., Bartelt-Hunt, S., Singh, P., & Singh, R. P. (2016). Biological response of using municipal solid waste compost in agriculture as fertilizer supplement. Reviews in Environmental Science and Bio/Technology, 15(4), 677-696.
Yogananda, S. B., Parama, V. R., Prakash, S. S., & Thimmegowda, M. N. (2019). Effect of biodegradable urban waste compost on growth and yield of maize (Zea mays L.). Indian Journal of Agricultural Research, 53(6).
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
Copyright (c) 2022 Agriculture and Environmental Science Academy

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.

