Assessment of physicochemical parameters and heavy metals concentration of leachates from dumpsite around Idemili River, Obosi Nigeria
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.26832/24566632.2025.1002025Keywords:
Correlation, Dumping sites, Heavy metals, Idemili River, LeachateAbstract
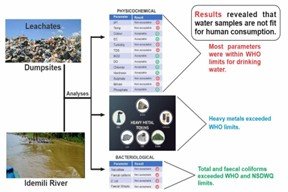
Leachates originating from solid waste dumpsites pollute water bodies, especially in Nigerian urban areas. This study aimed to assess the concentrations of heavy metals and physicochemical parameters in leachates from dumpsite around the Idemili River in Obosi, Nigeria. Physicochemical parameters (pH, temperature, EC, TDS, DO, BOD, turbidity, chloride, nitrate, phosphate, sulphate), heavy metals (Zn, Pb, Cd, Cu, Fe, As) and bacteriological parameters (total and faecal coliforms) were analyzed in leachate and Idemili River water. ANOVA, Tukey’s post-hoc and Pearson correlation were applied to find spatial variations and relationships between physicochemical properties and heavy metals concentration in leachate and water samples. Results revealed significant (p<0.05) contamination, with EC, sulphate, phosphate, nitrate, Fe, Cd and Pb in leachate samples exceeding WHO/NSDWQ limits. Leachate contained significantly higher levels of Fe (4.430±3.231 mg/L), As (4.455±3.1465 mg/L) and Cd (2.8783±2.794 mg/L), suggesting potential leachate infiltration, thereby influencing water quality. Also the leachate and water samples had elevated levels of total and faecal coliforms, exceeding the WHO standards of 10 cfu/mL and 0 cfu/mL, respectively. Results also revealed significant spatial variations in the physicochemical, heavy metals, and bacteriological parameters across various sampling points in leachate and water samples. Therefore, water samples from Idemili River are unsafe for human consumption, and aquatic ecosystems, due to leachates infiltration. It is recommended that governments should adopt inclusive approaches to reducing amount of wastes reaching dumpsites.
Downloads
References
Adewunyi, G. O., & Opasina, M. A. (2010). Physicochemical and heavy metals assessments of leachates from Aperin abandoned dumpsite in Ibadan City, Nigeria. Journal of Chemistry, 7(4):1278–1283. https://doi.org/10.1155/2010/401940
Agbozu, I. E., Oghama, O. E., & Odhikori, J. O. (2015). Physicochemical characterization and pollution index determination of leachates from Warri waste dumpsites, Southern Nigeria. Journal of Applied Sciences and Environmental Management, 19(3),361–372. https://doi.org/10.4314/jasem.v19i3.4
Akinrinlola, O., Ochonma, C., Akinrinlola, R., Adekojusola, O., & Ajayi, O. (2024). Assessment of the impact of dumpsites on groundwater quality in Osogbo metropolis, Nigeria. International Journal of Current Research in Applied Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, 3(2),15–23. http://science.eurekajournals.com/index.php/IJCRACCE/article/view/141
APHA. (2012). American Public Health Association: Standard methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater, Washington DC, USA, 1090.
Antai, S.P., Asitok, A.D., Tiku, D.R., & Louis, O.I. (2016). Microbiological analysis of solid waste biodegradation potential among selected isolates from municipal waste dumpsite in Calabar Municipality, Cross River State. International Journal of Innovative Science, Engineering and Technology, 3(11),447–472. https://doi.org/10.1003/ijiset.3.11.2016.472
Ashraf, M. A., Maah, M. J., & Yusoff, I. M. (2011). Heavy metals accumulation in plants growing in ex tin mining catchment. International Journal of Environmental Science and Technology, 8(2),401–416. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03326227
Ayadiuno, R. U., Mozie, A. T., & Ndulue, D. C. (2020). Mapping the terrain and land use types in Idemili South Local Government Area of Anambra State, South Eastern Nigeria. Ponte Multidisciplinary Journal of Sciences and Research, 76(9),122–134. https://doi.org/10.21506/j.ponte.2020.9.9
Azourgarh, Y. Abbaz, M., Hafid, N., Ez-Zahery, M., & El-Alem, N. (2019). Elimination of heavy metals (Cu, Zn, Cr, Ni and Pb) contained in the stabilized leachate of the Agadir landfill by percolation-infiltration on Titaniferous medium. Journal of Water Science and Environment Technologies, 4(1),460–464. https://www.ajol.info/index.php/jowset/article/view/276753
Bassey, I. U., Brooks, A., Asikong, B. & Andy, I. E. (2015). Environmental and public health aspects of solid waste management at the Lemna dump site in Calabar, Cross River State, Nigeria. International Journal of Tropical Diseases and Health, 10(3),1–13. https://doi.org/10.9734/ijtdh/2015/20023
Bassey, I. U., Andy, I. E., Unimke, A. A., & Akpanke, J. (2018). Hydrocarbon degrading potentials of Chromobacterium violaceum, Bacillus subtilis and Micrococcus luteus isolated from Lemna waste dumpsites, Cross River State, Nigeria. International Journal of Science and Research Publications, 8(11), 8317–8332. https://dx.doi.org/10.29322/IJSRP.8.11.2018.p8317
Bassey, I. U., Odokuma, L. O., Ogugbue, C. J., & Umejiaku, C. F. (2019). Hydrocarbon degradation potentials of bacterial species isolated from leachates of Lemna waste dumpsite, Calabar. International Journal of Science, Engineering and Technology Research, 8(6), 285–312. https://ijlsci.in/ls/index.php/home/article/view/834
Cheesbrough, M. (2010). District laboratory practice in tropical countries (2nd edn.). Cambridge University. Press. https://doi.org/10.1017/CBO9780511581304
Egbon, I. I., Okorie, T. G., & Imade, O. S. (2024). Seasonal evaluation of physicochemical parameters, heavy metals levels and pollution status in leachate from open solid waste dumpsite located in Benin City, Edo State, Nigeria. Journal of Applied Sciences and Environmental Management, 28(5), 1363–1371. https://doi.org/10.4314/jasem.v28i5.5
Ekeu-Wei, I. T., Azuma, K. I., & Ogunmuyiwa, F. B. B. (2018). Assessment of environmental impact of solid waste dumpsites using remote sensing. Nigerian Journal of Technology, 37(1), 275–285. https://doi.org/10.4314/njt.v37i1.36
Ezemonye, M.N., Ogbomida, E.T., Emeribe, C.N., Egharegbemi, O.O., & Emeribe, O.F. (2022). Impact of municipal solid waste dump sites on soil properties in Akure metropolis, Ondo State. Nigerian Journal of Life Sciences, 6(2),19–38. https://doi.org/10.52417/njls.v6i2.336
Ferreira, C. S., Adama-Ajonye, O., Ikenna, A. E., & Kalantari, Z. (2023). Groundwater quality in the vicinity of a dumpsite in Lagos metropolis, Nigeria. Geography and Sustainability, 4(4),379–390. https://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.geosus.2023.09.005
Förstner, U., & Wittmann, G. T. W. (1981). Metal pollution in the aquatic environment. Geological Magazine, 117(5), 500–501. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0016756800028661
Golden, A.H., & Inichinbia, S. (2020). Effect of landfill leachate on groundwater contamination: A case study of Obio/Akpor Local Government Area, Rivers State, Nigeria. Journal of Applied Sciences and Environmental Management, 24(8): https://doi.org/10.4314/jasem.v24i8.10
Ikpe, A. E., Owunna, I. B., & Agho, N. (2019). Physicochemical analysis of municipal solid waste leachate from open dumpsites in Benin City metropolis. Journal of Applied Sciences and Environmental Management, 23(1), 165–171. https://doi.org/10.4314/jasem.v2i1.24
Khatiebi, S., Siamba, D., Onyando, Z., Mulmbala, C., & Konje, M. (2018). Heavy metals contamination at dumpsites at Eldoret, Kenya, in the Lake Victoria Basin. African Journal of Tropical Hydrobiology and Fisheries, 16(2),93–97.
NSDWQ. (2017). Nigeria Standard for Drinking Water Quality (NSDWQ) and World Health Organization (WHO) Drinking Water Quality Standard for the Parameters. https://washnigeria.com/wp-content/uploads/2022/10/publications-Nigerian-Standard-for-Drinking-WaterQuality.pdf
Nwachi, A.C., Okoye, E.C.S., Nwakaeze, E.A., Elom, E.E., & Ogene, L.N. (2024). Molecular identification of biosurfactant-producing bacteria obtained from oil-polluted soil samples in Abakaliki, Ebonyi State, Nigeria. Archives of Agriculture and Environmental Science, 9(2), 367–372. https://dx.doi.org/10.26832/24566632.2024.0902023
Ocheoibo, S.J., & Atuanya, E.I. (2024). Evaluation of microbial load and physicochemical characteristics of soils in electronic waste dumpsites in Oluku and Osasogie in Benin, Edo State and Alaba in Lagos State. Journal of Applied Sciences and Environmental Management, 28(3), 953–960. https://doi.org/10.4314/jasem.v28i3.37
Okeh, A., Abu, M., Osagie, A.U., & Okwute, O.L. (2024). Comparative assessment of physicochemical and bacteriological parameters in water sources near major dumpsites and control areas in Karu-Abuja and parts of Nasarawa State. Asian Journal of Geological Research, 7(3), 471–502. https://doi.org/10.9734/ajoger/2024/v7i3182
Okiongbo, K. S., Oboshenure, K. K., & Amakiri, A. R. C. (2020). Investigation of lithological control of iron enrichment in groundwater using geophysical techniques in Yenagoa, Southern Nigeria. SN Applied Sciences, 2(1), https://doi.org/10.1007/s42452-019-1876-3
Okoye, E.C.S., Onuorah, S.C., Okoye, L.C., & Nwadiogbu, J.O. (2022). Effect of seasonal variations on the physicochemical characteristics of spring water in Oji River LGA, Enugu State, Nigeria. Archives of Agriculture and Environmental Science, 7(1),86–92. https://doi.org/10.26832/24566632.2022.0701012
Okoye, K. C., Ogunjiofor, E.I., Okoye, E. C. S., & Okoye, L.C. (2023). Impact of abattoir waste effluent on water bodies: A case study of Ugwuoba abattoir activities on Ezu River, Enugu State, Nigeria. International Journal of Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 5(2), 19–25.
Olagbemiro, T.O., Ekweozor, I. K. E., Ugbomeh, A. P., Ogbonna, D. N., Bob-Manuel, K. N. O., Green, F. A., & Nwibani, B. H. (2025). Assessment of physicochemical, heavy metals and microbial parameters in leachate and groundwater around solid waste dumpsites at Onne, Rivers State, Nigeria. Journal of Applied Science and Environmental Science, 29(3), 857–866. https://dx.doi.org/10.4314/jasem.v29i3.22
Olayiwola, H.A., Gbola, L.A., Adewuyi, K., & Azeez, M.O. (2017). Heavy metals contents in soils and plants at dumpsites: A case study of Awotan and Ajaknga dumpsite, Ibadan, Oyo State, Nigeria. Journal of Environmental and Earth Sciences, 7(4), 313–322.
Olukanni, D. O., Olujide, J. A., & Kehinde, E. O. (2017). Evaluation of the impact of dumpsite leachate on groundwater quality in a residential institution in Ota, Nigeria. Covenant Journal of Engineering and Technology, 1(1), 217–228.
Oluyori, A.O., & Oluyori, N.R. (2020). Spatial variation in pollution potential of leachate from dumpsites in the Federal Capital Territory, Nigeria. Journal of Resources, Forestry and Wildlife Environment, 12(2), 231–238.
Onwukeme, V. I., & Eze, V. C. (2021). Identification of heavy metals source within selected active dumpsites in Southeastern Nigeria. Environmental Analytical Health Toxicology, 36(2), e2021008. https://www.eaht.org/upload/pdf/eaht-36-2-e2021008.pdf
Saheed, I. O., Azeez, S. O., Jimoh, A. A., Obaro, V. A., & Adepoju, A. (2020). Assessment of some heavy metals concentration in soil and groundwater around refuse dumpsite in Ibadan metropolis, Nigeria. Nigerian Journal of Technology, 39(1), 301–305. http://dx.doi.org/10.4314/njt.v39i1.33
Salami, S. A., Ima-Ibizugbe, L. O., & Itiowe, K. (2024a). Physicochemical and heavy mineral characterization of soil and groundwater from Ekehuan (Asoro) dumpsite, Benin City. Environmental Technology and Science Journal, 15(1), 82–93. https://doi.org/10.4314/etsj.v15i1.9
Salami, S.A., Omoniyi, M.E., & Itiowe, K. (2024b). Geo-environmental assessment of the impacts of Ewu-Elepe dumpsite on soil and groundwater resources at Ikorodu, Lags State, Nigeria. Dutse Journal of Pure and Applied Sciences, 10(1), https://doi.org/10.4314/dujopas.v10i1b.26
Titilawo, Y., Adeniji, A., Adeniji, M., & Okoh, A. (2018). Determination of levels of some metal contaminants in the freshwater environments of Osun State, Southwest, Nigeria: A risk assessment approach to predict health threat. Chemosphere, 211, 834–843. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2018.07.203
Ugbaja, A. N., Ugbaja, U. A., Nwosu, S. U., & Nyong, V. E. (2021). Physicochemical evaluation of groundwater near Ikot Effanga dumpsite, Calabar, Southeastern Nigeria. Global Journal of Geological Sciences, 19(1), 75–84. https://doi.org/10.4314/gjgs.v19i1.6
UNEP, United Nations Environment Programme (2024). Global waste management outlook: beyond an age of waste – Turning rubbish into a resource. United Nations Environment Assembly (UNEA), Resolution 4/7, 4th session, Sweden. https://www.unep.org/resources/global-waste-management-outlook-2024
USEPA, United States Environment Protection Agency (2013). Wastes–non-hazardous wastes – municipal solid waste. Washington DC, USA. https://archive.epa.gov/epawaste/nonhaz/municipal/web/html/
WHO. (2017). Guidelines for drinking water quality. 4th edition, WHO Press, Geneva Switzerland. https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/9789241549950
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Agriculture and Environmental Science Academy

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.




